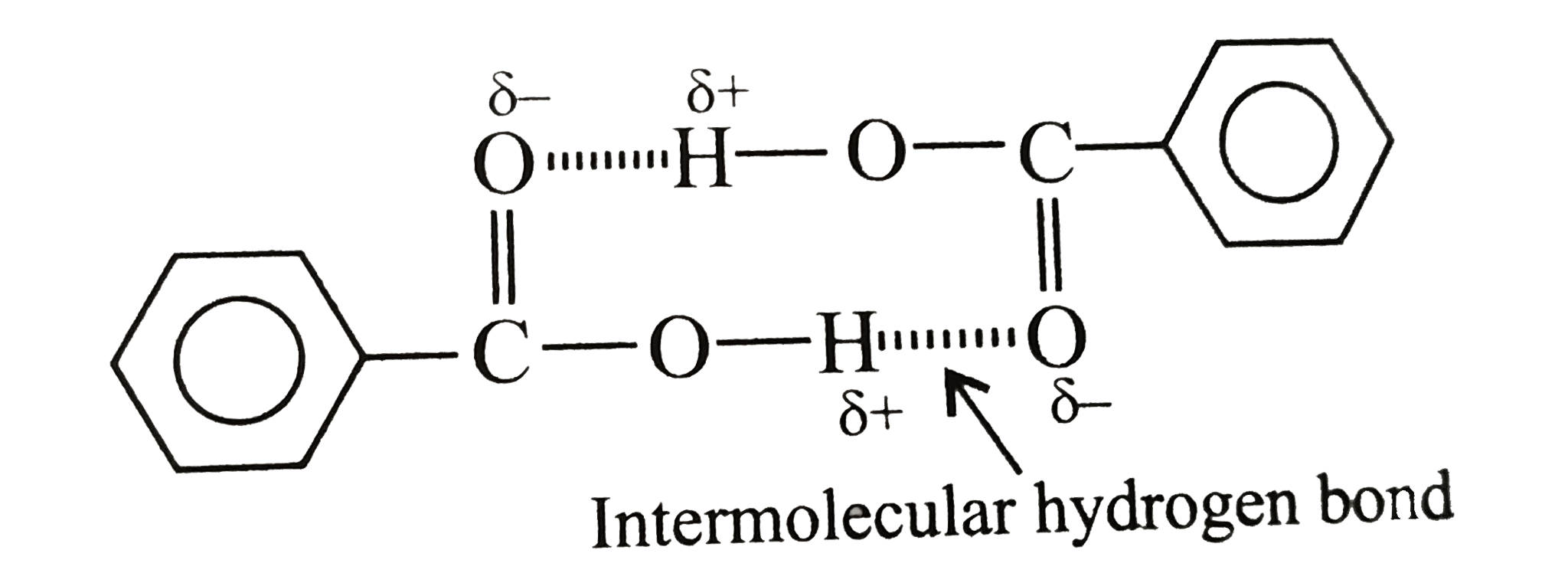
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- When 1.22 g C(6)H(5)COOH is added into two solvents, the following dat...
Text Solution
|
- 1g of same non volatile solute is added to 100g of two different solve...
Text Solution
|
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in acetone and benzene separately....
Text Solution
|
- 1.22 g of benzoic acid is dissolved in 100 g of acetone and 100 g of a...
Text Solution
|
- If 30g of a solute of molecular weight 154 is dissolved in 250 g of be...
Text Solution
|
- After adding non-volatile solute, freezing point of water decreases to...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C, C(6)H(8)O(6)) to be d...
Text Solution
|
- अवाष्पशील विलेय मिलाने पर जल का हिमांक बिंदु -0.186^(@)C कम हो जाता है...
Text Solution
|
- Ratio of (DeltaT(b))/(K(b)) of 10 g AB(2) and 14g A(2)B per 100 g of s...
Text Solution
|