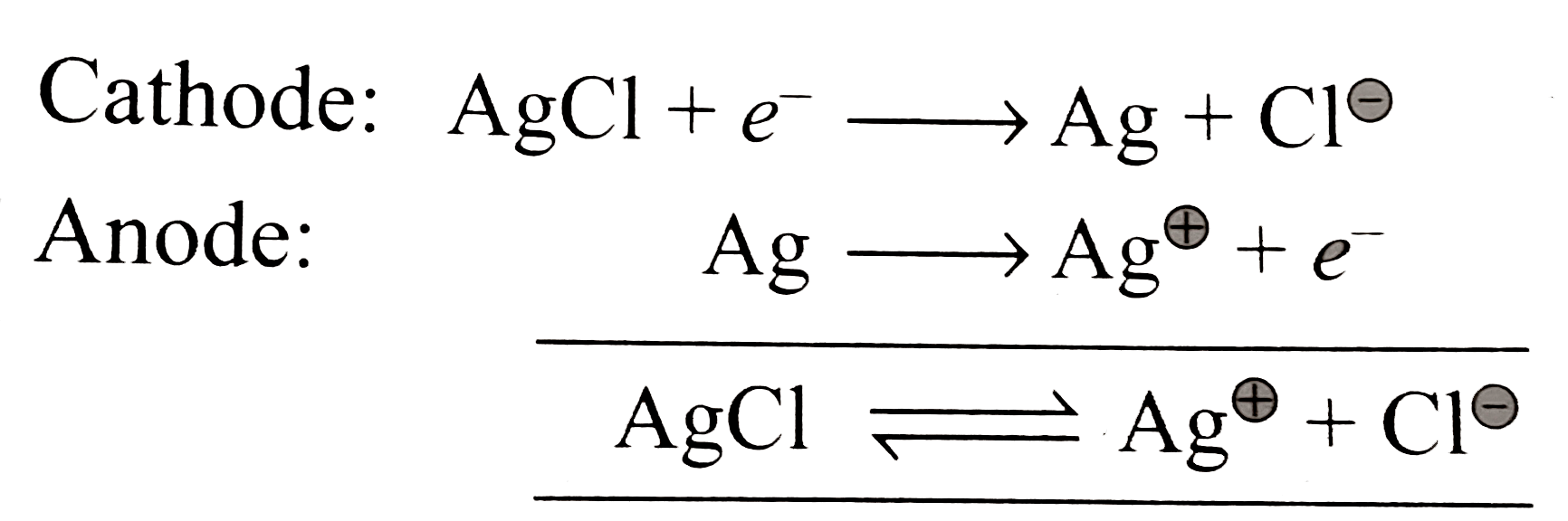A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The standard electrode of a metal ion (Ag|Ag^(o+)) and metal - insolu...
Text Solution
|
- Find the solubility of AgCl in 0.1 M CaCl(2) . E^(c-).(Ag^(o+)|Ag)=0.7...
Text Solution
|
- The standard electrode of a metal ion (Ag|Ag^(o+)) and metal - insolu...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the electrode Ag|AgCl(s),Cl^(c-)(0.1M),i.e., silver electrode...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of Cl^(c-)|AgCl|Ag half cell is related to that...
Text Solution
|
- Metal Insoluble Salt Anion Electrode
Text Solution
|
- The standard electrode potential of the electrode Ag(s) , AgCl| KCl (1...
Text Solution
|
- The standard reduction potential of Ag^(+)|Ag electrode is 0.80 volt. ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the K(sp) of AgCl from the following data. The standard electrode...
Text Solution
|