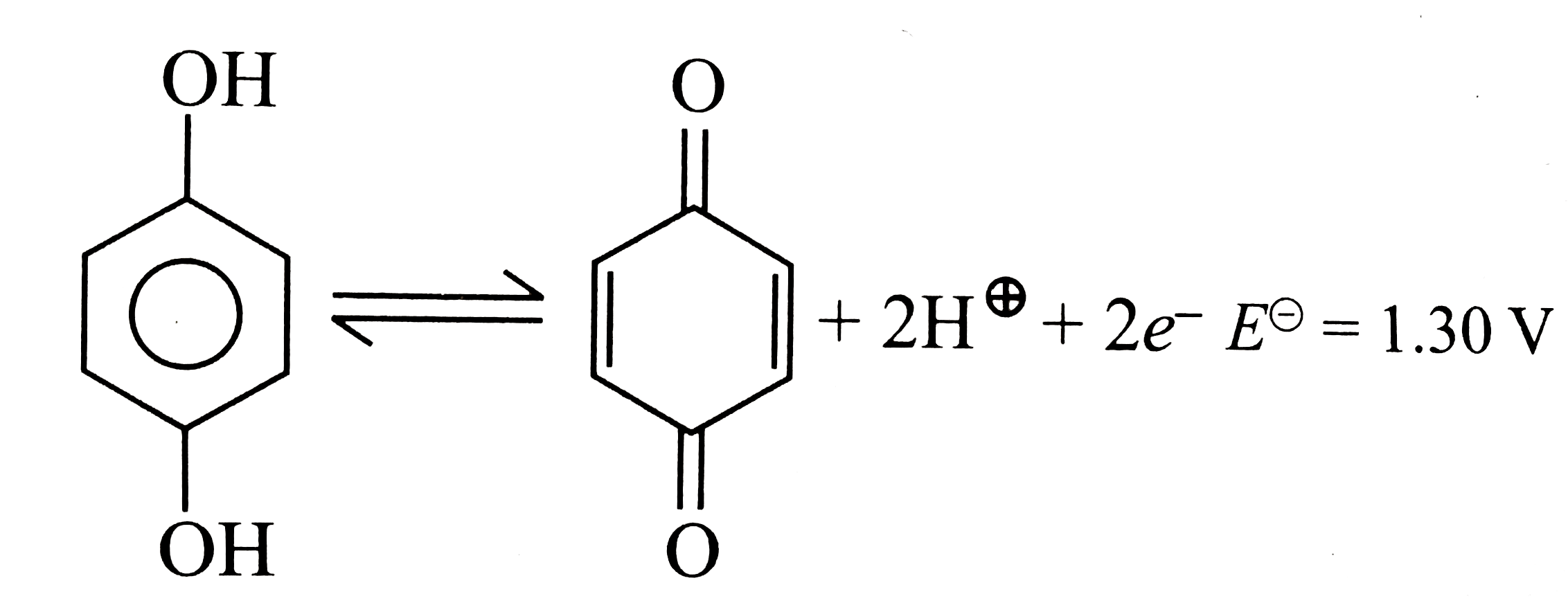
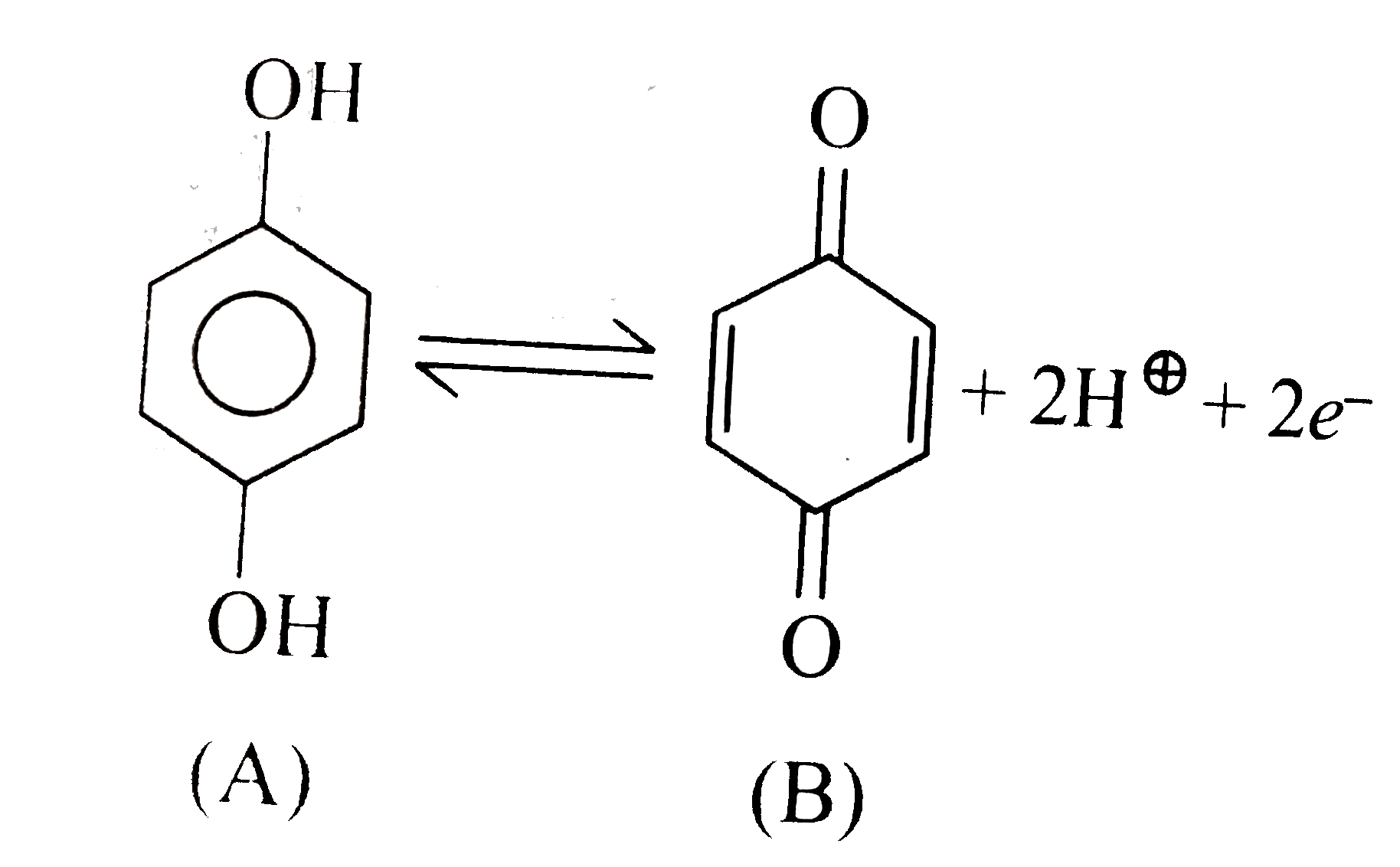A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For the half cell At pH=2, the electrode potential is
Text Solution
|
- For the half cell At pH=2, the electrode potential is
Text Solution
|
- The half-cell reduction potential of a hudrogen electrode at pH= 10 wi...
Text Solution
|
- For the half cell At pH=2. Electrod potential is :
Text Solution
|
- For the half cell At pH = 3 electrode potential is
Text Solution
|
- अर्ध्द –सेल का इलेक्ट्रोड विभव निर्भर करता हैं-
Text Solution
|
- The electrode potential of oxidation half cell
Text Solution
|
- The electrode potential of oxidation half cell
Text Solution
|
- For the half cell, +2H^(+)2e^(-).E^(0)= 1.30 V. At pH = 2, elec...
Text Solution
|