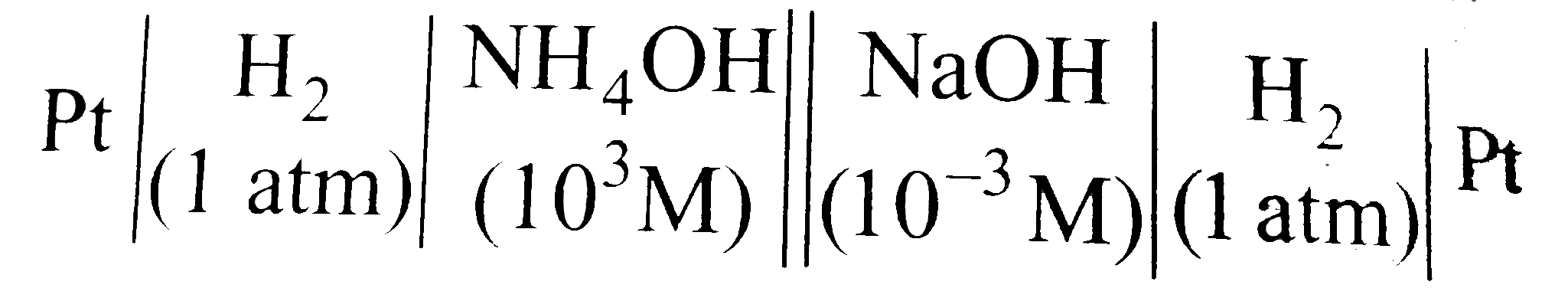A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The potential the cell at 25^(@)C is Given pK(b) of NH(4)OH=4.74
Text Solution
|
- Given the following cell at 25^(@)C What will be the potential of the ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential the cell at 25^(@)C is Given pK(b) of NH(4)OH=4.74
Text Solution
|
- The potential of the cell at 25^(@)C is Given pK(a) of CH(3)COOH and p...
Text Solution
|
- Amount of (NH(4))(2)SO(4) which must be added to 50mL of 0.2 M NH(4)OH...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the pH of the following mixture 50mL of 0.05M CH(3)COOH+50...
Text Solution
|
- 60ml of 0.1M NH(4)OH is mixed with 40 ml of 0.1M HCl . Which of the fo...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the degree of dissociation of 0.005M NH(4)OHsolution. If ...
Text Solution
|
- In which volume ratio NH(4)Cl and NH(4)OH solutions (each 1 M ) should...
Text Solution
|