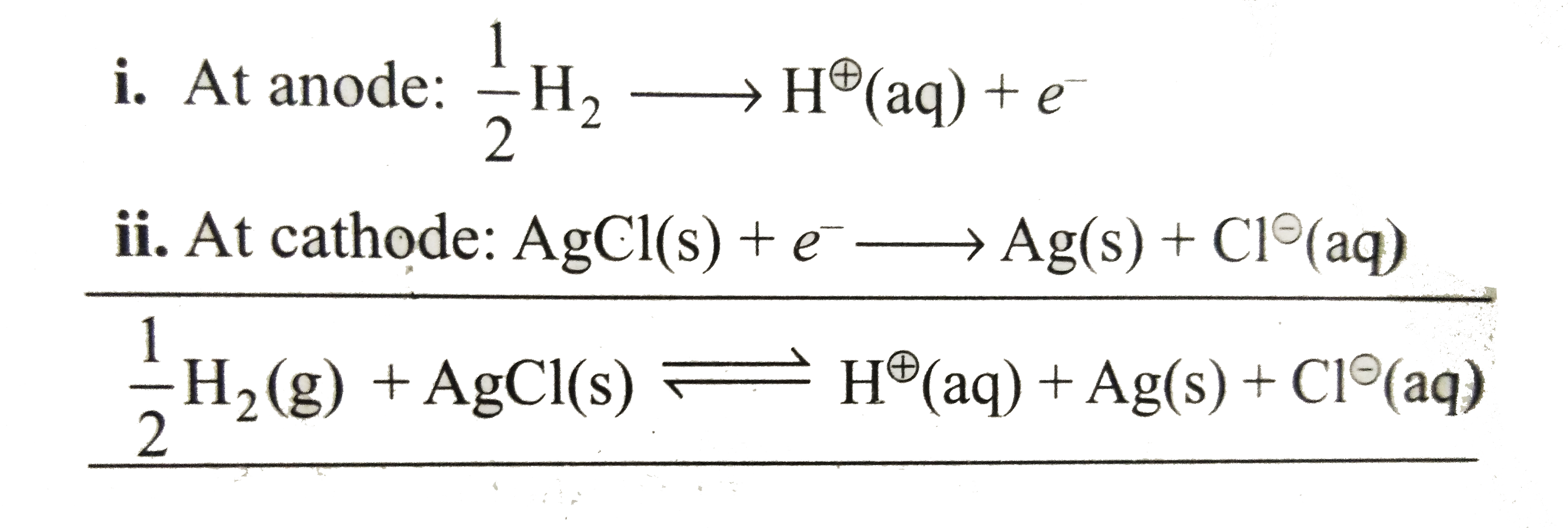Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23V at 15^(@)C and 0...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23V at 15^(@)C and 0...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at 15^(@)C and...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at 15^(@)C and ...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at 15^(@)C and ...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at 15^(@)C and ...
Text Solution
|
- The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at 15^(@)C and ...
Text Solution
|
- E.M.F. of following cell is 0.265 V at 25^@C and 0.2595 V at 35^@C. Ca...
Text Solution
|
- The emf of the following cell is 0.256 V at 25^@C and 0.2595 V at 35^@...
Text Solution
|