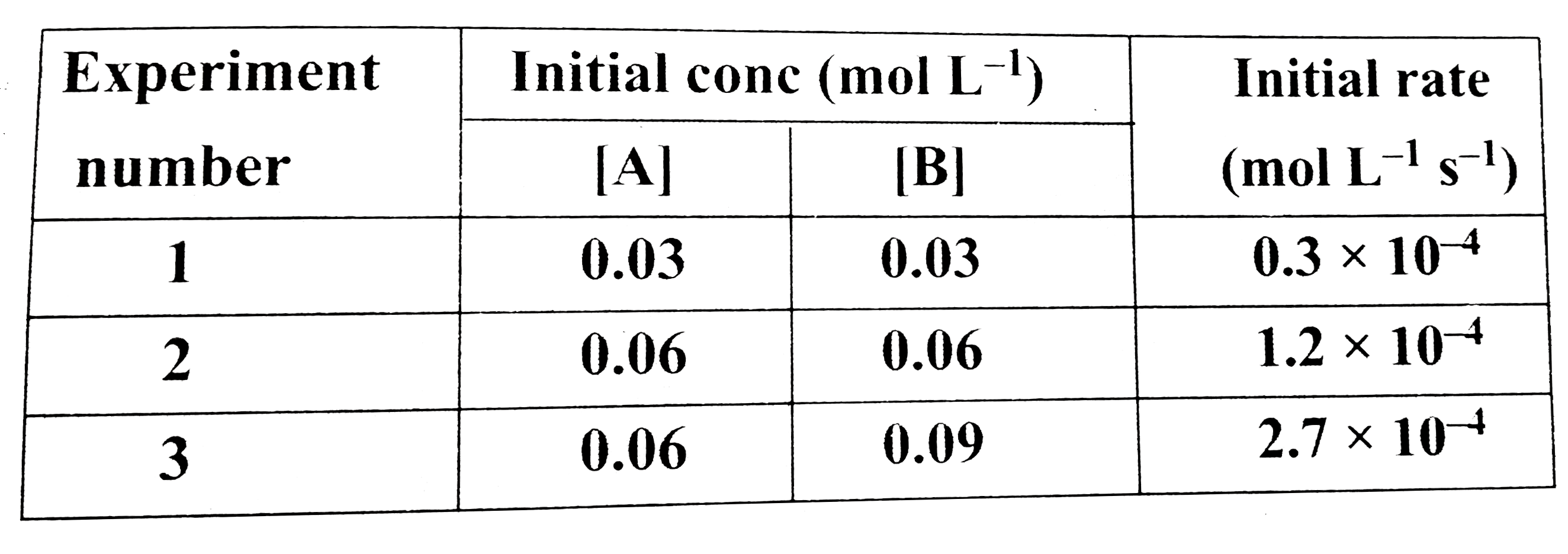Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For a reaction in which A and B form C, the following data were obtain...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction in which A and B form C, the following data were obtain...
Text Solution
|
- For the given reaction A+B rarr Products, the following data are g...
Text Solution
|
- The following rate data were obtained at 303 K for the following react...
Text Solution
|
- The following initial rate data were obtained at 300K for the reaction...
Text Solution
|
- Rate of a reaction is given by the equation : Rate =k[A]^(2)[B] What a...
Text Solution
|
- For the given reaction, A + B rarr Products Following data are given (...
Text Solution
|
- At T(K), the following data were obtained for a general reaction, A + ...
Text Solution
|
- Rate of a reaction is given by the equation: Rate = k[A]^2[B]. What ar...
Text Solution
|