Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-MODEL PAPER 5-SECTION - B
- What are n-type and p-type semiconductors?
Text Solution
|
- Calculate molality of 2.5 of ethanoic acid (CH(3)COOH) in 75g of benze...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the structure of TMV.
Text Solution
|
- Explain Werner's theory. Give the Werner's structures of CoCl3. 6NH3 ,...
Text Solution
|
- Give the sources of the following vitamin and name the diseases cause...
Text Solution
|
- Explain froth flotation process with neat diagram.
Text Solution
|
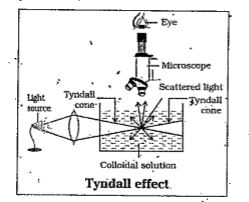
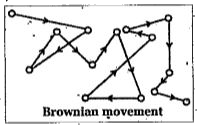
- Explain Tyndall effect and Brownian movement.
Text Solution
|
- Explain sp^2 hybridization with an example.
Text Solution
|