The device in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy is called galvanic ceffor electrochemical cellof voltaic cell. In a galvanic cell, a redox reaction is carried in an indirect manner and the decrease in free energy during the chemical process is made to appear as electrical energy.
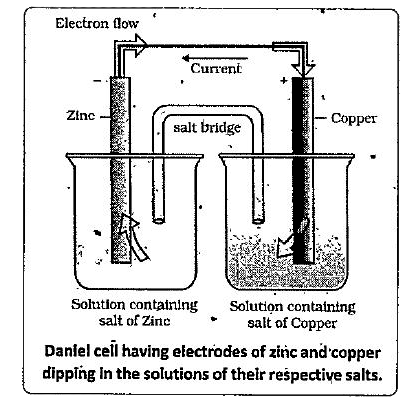
In the Daniel cell a zinc strip is dipped in the `ZnSO_(4)` solution and a copper strip is dipped in the `CuSO_(4)` solution taken in separate beakers. The two metallic strips which act as electrodes are connected by the conducting wires through Voltmeter. The two solutions are joined by an inverted U - tube known as salt bridge which contain an electrolyte such as KCI, KNO, or `NH_(4)Cl` along with gelatin or agar-agar to convert the electrolyte into semi solid.paste. . The working of the cell can be .understand by the following steps.
i). Zinc undergoes oxidation to form zinc ions
`Z(s) to Zn^(2+) (aq)+2e^(-)` oxidation
The electrons liberated during oxidation are pushed through the vconnecting wires, to copper strip
(iii) Copper ions move towards coppers strip pick up the electrons and get reduced to coper atoms which are deposited at the coper strip.
`Cu^(2+)(aq)+2e^(-) to Cu (s)` Reduction.
he transference of electrons from anode (oxidation electrode i.e., zinc electrode) to cathode (reduction electrode i.e., copper electrode) leads to flow of electric current.
Problem:
`DeltaG_(n)^(Ɵ)=-nF E_("cell")^(Ɵ)`
`n=2F=96487 C"mol"^(-1), E_("cell")^(Ɵ)=1.1V`
`:. DeltaG_(n)^(Ɵ)=-2xx1.1Vxx96487 "C mol"^(-1)`
`=-21227 " J mol"^(-1)=-212.27 "KJ mol"^(-1)`
