On a large scale, ammonia is manufactured by Haber.s process.
`N_(2)(g)+3H_(2)(g) hArr 2NH_(3)(g), Delta_(f)H^(@)=-46.1 "KJ mol"^(-1)`
The optimum conditions for production of ammonia are a pressure of about `2000 xx 10^(5)` Pa and a temperature of 700K. Iron oxide is the catalyst with small amounts of `K_(2) O and Al_(2)^(3)`
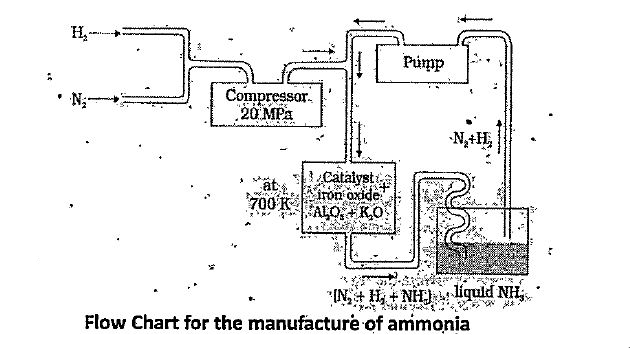
Flow Chart for the manufacture of ammonia
Compressed mixture of `N_(2)` and `H_(2)` in the volume ratio is heated. to 700K at a pressure of 200 atmand passed over finely divided iron oxide mixed with samll amounts of `K_(2)O and Al_(2)O_(3)` Ammonia formed is liquifid and unreacted mixture of `N_(2) and H_(2)` again pumped into catalytic chamber
`XeO_(3)` is prepared by the hydrolysis of `XeF_(6)`
`XeF_(6)+3H_(2)O to XeO_(3)+6HF`
Partial hydrolysis of `XeF_(6)` gives oxyfluorides.
`XeF_(6)+H_(2)O to XeOF_(4)+2HF`
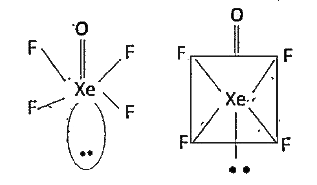
`X_(2)O_(3)` : Xe undergoes `sp^(3)` hybridisation
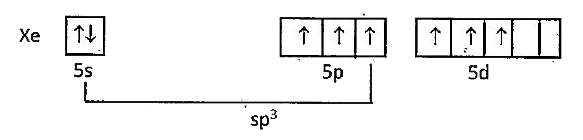
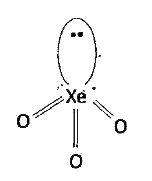
Unpaired electrons in d-orbital form `dpi-p pi` A bonds with oxygen. `sp^(3)` orbitals form `3 sigma` bonds with oxygen-atoms. Because of the presence of lone pair, the molecule assumes pyramidal shape with a bond angle of `103^(@)`
`XeOF_(4)` Partial hydrolysis of `XeF_(6)` gives oxygluorides.
`XeF_(6)+H_(2)O to XeOF_(4) +2HF`
`XeOF_(4)` has square pyramidal.