A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
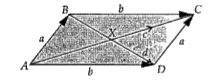
- ABCD is a parallelogram whose adjacent sides are represented by the ve...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the point of symmetry of a regular hexagon. <img src="htt...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Column A to Column B
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Column A to Column B
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Column A to Column B
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the figure given below.
Text Solution
|
- The area of the shaded part in the figure given below is .
Text Solution
|
- The inequation represented by the graph given below is : <img src="htt...
Text Solution
|
- The inequation that best describes the graph given below is <img src=...
Text Solution
|