Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA TPC JEE MAIN TEST 111-PHYSICS
- In the figure a smooth pulley of negligible weight is suspended by a s...
Text Solution
|
- A Galvanometer, with a scale divided into 150 equal divisions, has cur...
Text Solution
|
- A sound wave of frequency f propagasing through air with a velocity C,...
Text Solution
|
- Two stationary soruces of sound, S(1) and S(2) having an equal frequen...
Text Solution
|
- An incompressible liquid travels as shown in figure. Calculate the spe...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray moving in medium-I (of refractive index n(1)) is incident ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass M kg and length L m is bent in the from of an equilatera...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular ring of mass M and radius R is rotating about its a...
Text Solution
|
- The specific heats, C(P) and C(V) of a gas of diatomic molecules, A ar...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's experiment , the fringe width of the fringes with light of ...
Text Solution
|
- When the first transitions of the Balmer series of excited hydrogen at...
Text Solution
|
- All the edges of a block with parallel faces are unequal. Its longest ...
Text Solution
|
- A bandwidth of 10 MHz is available for AM transmission. If the maximum...
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of |vecV| if the linear velocity of a rotating body is ...
Text Solution
|
- A tightly wound solenoid of radius 'a' and length 'l' has n turns per ...
Text Solution
|
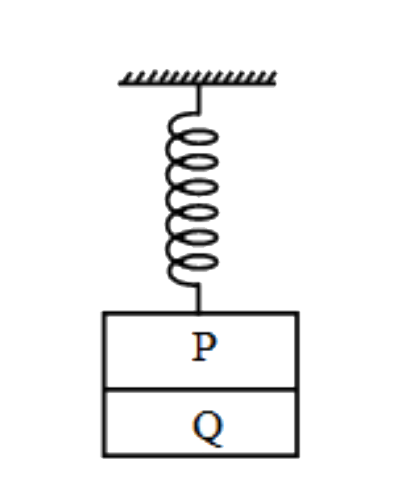
- Two blocks P and Q of masses 0.3 kg and 0.4 kg respectively are stuck ...
Text Solution
|
- The lengths of sides of a cuboid are a, 2a and 3a. If the relative per...
Text Solution
|
- A light rod of length 4.0 m is suspended from the ceiling horizontally...
Text Solution
|
- Earth receives 1400 W m ^-2 of solar power. If all the solar energy fa...
Text Solution
|
- An automobile travelling with a speed 60 km//h , can brake to stop wi...
Text Solution
|