Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
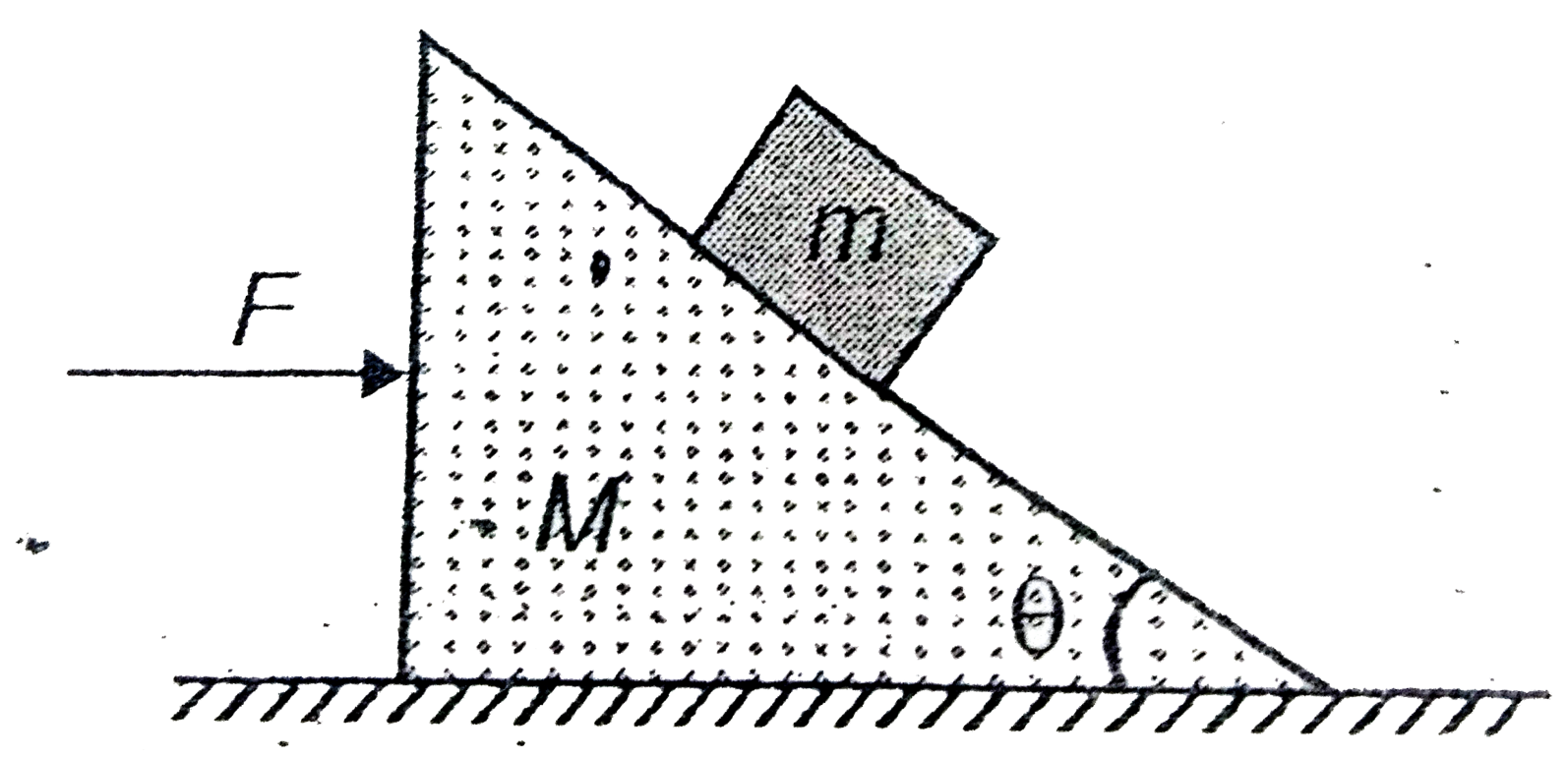
- A block of mass m is placed on a wedge of mass M and a force F is acti...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is in equilibrium relative to the smooth wedge of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth blocks of masses m and m' connected by a light inextensible...
Text Solution
|
- Figure-2.52 shows a box of mass m is placed on a wedge of mass M on a ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a wedge of mass M and a force F is acti...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a wedge of mass M and a force F is act...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, all surfaces are smooth and the pulley is massles...
Text Solution
|
- All the surfaces are smooth as shown in figure. The acceleration of ma...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, the wedge is acted upon by a constant horizontal ...
Text Solution
|