To solve the problem, we need to analyze the given wave equation and determine the plot of \( y \) versus \( x \) at \( t = 10 \, s \).
### Step-by-Step Solution:
1. **Understand the Wave Equation**:
The wave is described by the equation:
\[
y = 5 \, \text{mm} \, e^{\left(\frac{T}{5 \, s} - \frac{x}{5 \, cm}\right)^2}
\]
Here, \( T \) is the time variable, \( x \) is the position along the string, and \( e \) is the base of the natural logarithm.
2. **Substitute the Given Time**:
We are asked to find the plot at \( t = 10 \, s \). Substitute \( T = 10 \, s \) into the equation:
\[
y = 5 \, \text{mm} \, e^{\left(\frac{10 \, s}{5 \, s} - \frac{x}{5 \, cm}\right)^2}
\]
Simplifying this gives:
\[
y = 5 \, \text{mm} \, e^{\left(2 - \frac{x}{5 \, cm}\right)^2}
\]
3. **Analyze the Exponential Term**:
The term \( \left(2 - \frac{x}{5 \, cm}\right)^2 \) indicates that the wave will have a maximum value when the argument of the exponential function is zero. This occurs when:
\[
2 - \frac{x}{5 \, cm} = 0 \implies x = 10 \, cm
\]
4. **Determine the Maximum Value of \( y \)**:
At \( x = 10 \, cm \):
\[
y = 5 \, \text{mm} \, e^{0} = 5 \, \text{mm}
\]
This is the maximum value of \( y \).
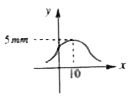
5. **Behavior of the Function**:
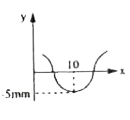
As \( x \) moves away from \( 10 \, cm \), the value of \( y \) will decrease rapidly due to the nature of the exponential function. The plot will show a peak at \( x = 10 \, cm \) and will taper off as \( x \) moves away from this point.
6. **Plotting the Function**:
The plot of \( y \) versus \( x \) at \( t = 10 \, s \) will show a Gaussian-like shape centered at \( x = 10 \, cm \) with a maximum height of \( 5 \, mm \).
### Conclusion:
The plot of \( y \) versus \( x \) at \( t = 10 \, s \) is best indicated by a Gaussian curve peaking at \( x = 10 \, cm \) with a maximum value of \( 5 \, mm \).