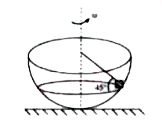
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A hemispherical bowl is rotated about the axis shown with constant ang...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moves along line PC with velocity v as shown. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- A particle mass parallel to x-axis with constant velocity v as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circle with constant angular velocity omega abou...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P will be in equilibrium inside a hemispherical bowl of rad...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius 0.1m is rotated about a vertical axis p...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius r is rotated with an angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|