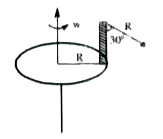
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A disc of radius (R) has a light pole fixed perpendicular to the disc ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R has linear velocity v and angular velocity omega as...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R is rolling without sliding on a horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of radius R is rotating about its own axis wit...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R has a light pole fixed perpendicular to the disc at...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius a is ridigly attached at its circumference to a rod o...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R is rotating in a horizontal plan...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating with angular veloci...
Text Solution
|
- A disc has mass 'M' and radius 'R'. How much tangential force should b...
Text Solution
|