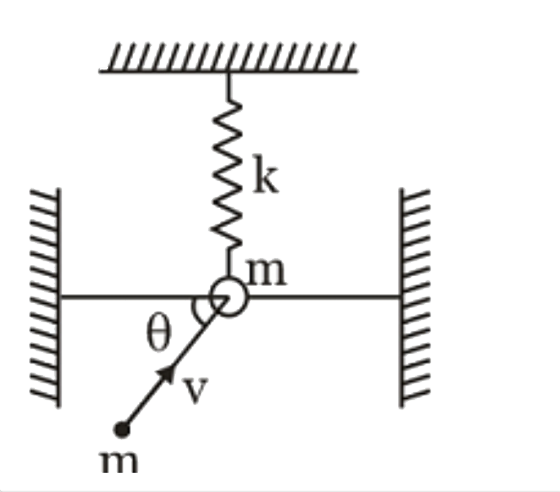
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An underformed spring of spring constant k is connected to a bead of m...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass M moving on the frictionless horizontal surface col...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m collides elastically with the pan of mass (M = 2m...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass m is connected to a spring of spring constant k and a st...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is released when the spring was in its natrual len...
Text Solution
|
- An underformed spring of spring constant k is connected to a bead of m...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m moves with a speed v on a horizontal smooth surface and colli...
Text Solution
|
- Two springs are connected to a block of mass M is placed on a friction...
Text Solution
|
- An underformed spring of spring constant k is connected to a bead of m...
Text Solution
|