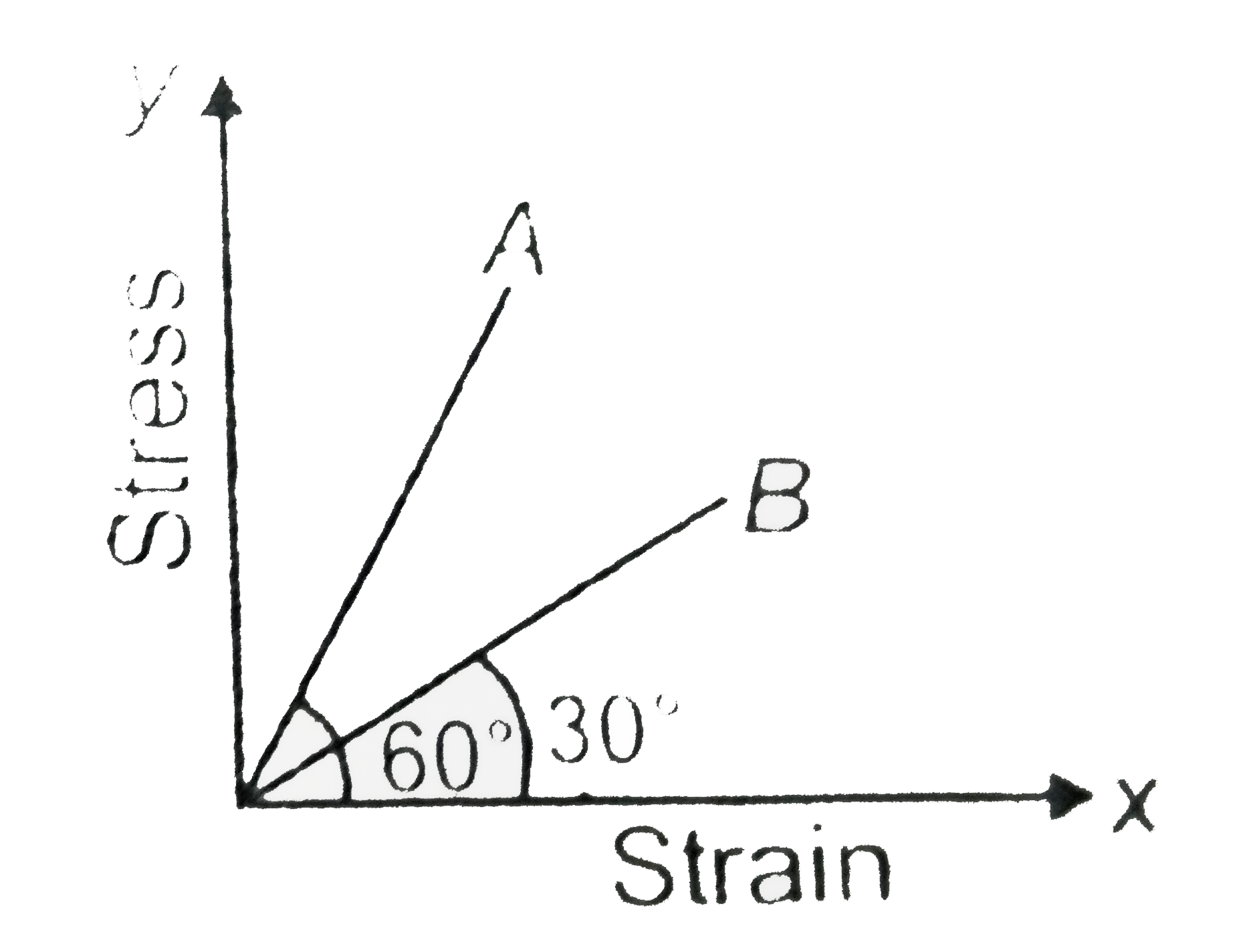
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The stress versus strain graph for wires of two materials A and B are ...
Text Solution
|
- The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials A and B are...
Text Solution
|
- The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials A and B are...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of the same length l and radius are joined end to end and lo...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 9.11 shown the strain - stress curve for a given material. What...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 9.11 shown the strain - stress curve for a given material. What...
Text Solution
|
- The stress versus strain graph for two materials A and B are shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- दो पदार्थो A तथा B के तारों के लिए प्रतिबल तथा विकृति के बीच ग्राफ चित...
Text Solution
|
- The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B The graphs are drawn to...
Text Solution
|