Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-WAVES-EXERCISE-III (Doppler effect :)
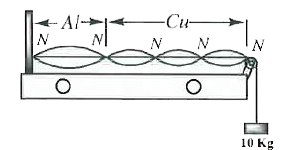
- An aluminium wire of cross-sectional area (10^-6)m^2 is joined to a st...
Text Solution
|
- When a train is approaching the stationary observer, the apparent freq...
Text Solution
|
- Two sources A and B are sounding notes of frequency 680 Hz. A listener...
Text Solution
|
- Two different sound sources s1 and so have frequencies ratio 1:2. Sour...
Text Solution
|
- A siren placed at a railway platfrom is emitted sound of frequency 5 k...
Text Solution
|
- A train moves towards a stationary observer with speed 34 m/s. The tra...
Text Solution
|
- A police car moving at 22(m)/(s) chases a motorcyclist. The police man...
Text Solution
|
- A train is moving at 30 m/s in still air. The frequency of the locomot...
Text Solution
|
- A siren emitting a sound of frequency 2000 Hz moves away from you towa...
Text Solution
|
- A car travelling at a speed of 8 m/s towards a large wall horns a soun...
Text Solution
|
- The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the frequency of the waves given below.
Text Solution
|
- A whistle of frequency 540 Hz rotates in a horizontal circle of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A bat moving at 10 ms^(-1) towards a wall sends a sound signal of 8000...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars moving in opposite directions approach each other with speed ...
Text Solution
|
- A tuning fork is used to produce resonance in a glass tube. The length...
Text Solution
|