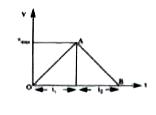
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A bus accelerates from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time, af...
Text Solution
|
- A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time, af...
Text Solution
|
- A bus accelerated from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time, af...
Text Solution
|
- A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate for some time after whi...
Text Solution
|
- A car at rest accelerates at a constant rate alpha for sometime after ...
Text Solution
|
- A bus accelerates from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time, af...
Text Solution
|
- A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time, af...
Text Solution
|
- A bus accelerates from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time,aft...
Text Solution
|
- A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate alpha for some time,aft...
Text Solution
|