Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
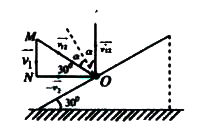
- A ball A is falling vertically downwards with velocity v(1) . It strik...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure block moves downwards with velocity v(1), the wedge righ...
Text Solution
|
- In fig., blocks A and B move with velocities v(1) and v(2) along horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass m is projected with a minimum horizontal velocity...
Text Solution
|
- Three block 1, 2 and 3 are arranged as shown in the figure. The veloci...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure a body of mass m moving horizontally with spee...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m=1kg falling vertically with a velocity v(0)=2m//s str...
Text Solution
|
- A ball A is falling vertically downwards with velocity v(1) . It strik...
Text Solution
|
- The slope of wind screen of two cars are alpha(1)=30^(@) and a(2)=15^(...
Text Solution
|