Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Assess Your Self|13 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Exercise-I|80 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE EXERCISEX|42 VideosELECTRIC FIELD AND POTENTIAL
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PROBLEMS (LEVEL-II)|26 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS-Practice Exercise
- A ray of light falls normally on a rectangular glass slab. Draw a ra...
Text Solution
|
- When charge is given to a body
Text Solution
|
- Calculate force between two charges of 1C each separated by 1m in vacu...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal and opposite charges are placed at a certain distance apart ...
Text Solution
|
- Two positively charged small particles, each of mass 1.7 xx 10^(-27) k...
Text Solution
|
- The minimum electrostatic force between two charged particles placed a...
Text Solution
|
- The force between two alpha-particles separated by a distance .r. is F...
Text Solution
|
- The force between two charges 0.06m apart is 5N. If each charge is mov...
Text Solution
|
- Four point charges qA = 2 µC, qB = –5 µC, qC = 2 µC, and qD = –5 µ C a...
Text Solution
|
- The force between two charges separated by a distance 1m is 1.8N. The ...
Text Solution
|
- In 1 gram of solid, there are 5 xx 10^(21) atoms. If one electron is r...
Text Solution
|
- Two positively charged particles each of mass is 9 xx 10^(-30)kg and c...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is divided into two charge q and Q-q. The value of q such t...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the forces between two charges placed at a certain distan...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges +2C and +6C repel each other with a force of 12N. If...
Text Solution
|
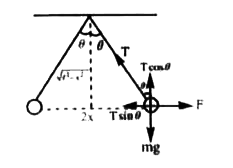
- Two small balls having equal positive charge Q (coulumb) on each suspe...
Text Solution
|
- The force between two charges 4C and -2C which are separated by a dist...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges 9 mu C and 1mu C are placed at a distance of 30cm. The pos...
Text Solution
|
- Three point charges Q(1), Q(2) and Q(3) in that order are placed equal...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid having n = 200 turns per metre has a circular cross-se...
Text Solution
|
- 10C and 20C are separated by a distance d. If the electric field at th...
Text Solution
|