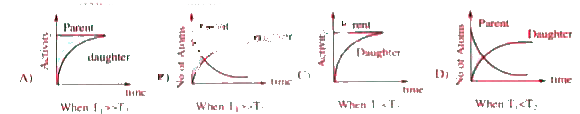A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NUCLEAR PHYSICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE LEVEL-II (LECTURE SHEET (ADVANCED)) More than one correct answer Type Questions )|4 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE LEVEL-II (LECTURE SHEET (ADVANCED)) Linked Comprehension Type Questions Passage-I :)|2 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL-I (MAIN)) (Straight Objective Type Questions)|10 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE-III|49 VideosNUCLEI
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Exercise|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-NUCLEAR PHYSICS-ADDITIONAL PRACTICE LEVEL-II (LECTURE SHEET (ADVANCED)) Straight Objective Type Questions )
- Nucleus A decays into B with decay constant lambda(1) and B decays int...
Text Solution
|
- At time t=O, some radioactive gas is injected into a sealed vessel. At...
Text Solution
|
- A nucleus .A. decays into .b. with half life .T(1). and B decays into ...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that the nuclear binding energy per nucleon (B/A) versus mass n...
Text Solution
|
- A radio nuclide A(1) with decay constant lambda(1) transforms into a r...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive nucleus undergoes a series of decay according to the sch...
Text Solution
|
- Binding energy per nucleon of 1^(H^(2)) and 2^(He^(2)) are 1.1 MeV and...
Text Solution
|
- The energy equivalent to 1 amu is?
Text Solution
|
- Calculate output of .(92)^(235)U reactor, if it takes 30 days to use u...
Text Solution
|