A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
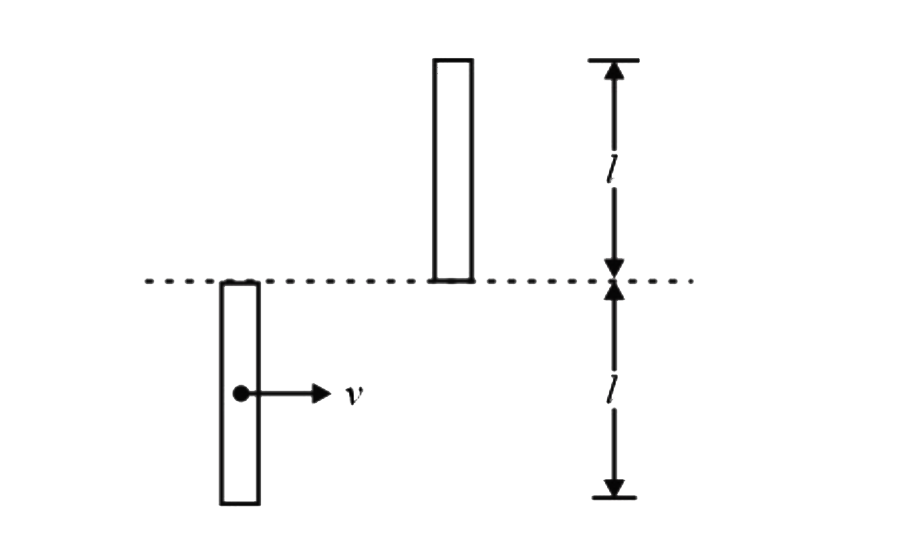
- A bar of mass m and length l is in pure translational motion with its ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8m lies on a smooth horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8m lies on a smooth horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass 'm' length 'l' is in pure translatory motion with its ce...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8m lies on a smooth horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass M and length L is in pure traslatory motion with its of ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar lies on a frictionless horizontal surface and is fr...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8 m lies on a smooth horizontal ta...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar of length L and mass 8m lies on a smooth horizontal...
Text Solution
|