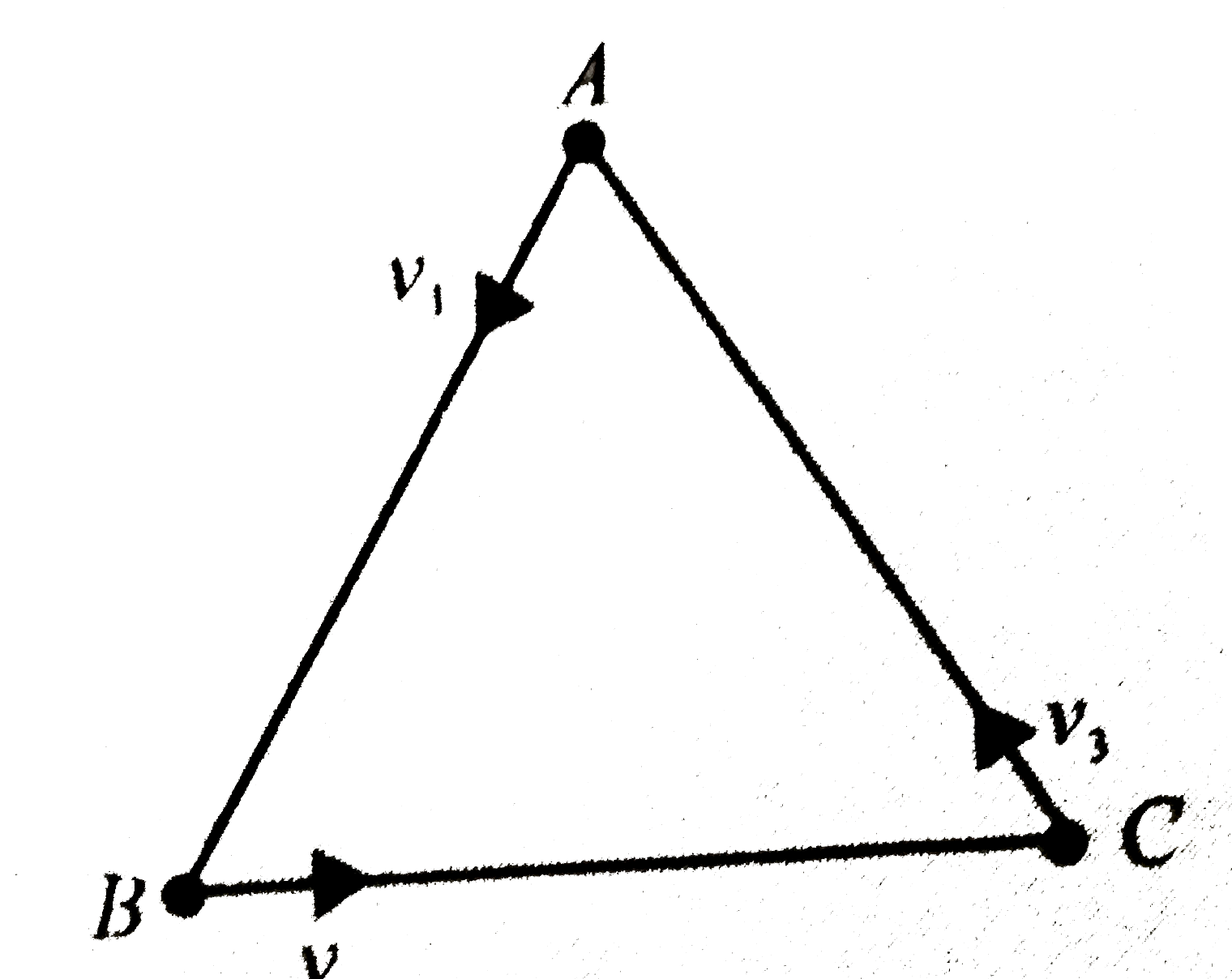A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Let there are three equal masses situated at the vertices of an equila...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles A,B, and C are situated at the vertices of an equilate...
Text Solution
|
- Let there are three equal masses situated at the vertices of an equila...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles of equal masses are placed at the corners of an equila...
Text Solution
|
- किसी कण के सापेक्ष वेग क्या अभिप्राय है ? दो कण A तथा B एक सीधी सड़क...
Text Solution
|
- तीन कण A , B और C किसी समय t = 0 पर d भुजा वाले समबाहु ABE के शीर्ष ...
Text Solution
|
- दो कणो A तथा B के विस्थापन - समय ग्राफ सरल रेखाएँ है जो समय अक्ष से क्...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles start from the origin at the same time, one with a vel...
Text Solution
|
- A particle starting from a point A and moving with a positive constant...
Text Solution
|