Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
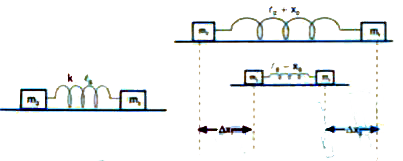
- Two masses m1 and m2 re connected by a spring of spring constant k and...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m1 and m2 re connected by a spring of spring constnt k and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bars of masses m1 and m2 connected by a weightless spring of stiff...
Text Solution
|
- In an ideal pulley particle system, mass m2 is connected with a vertic...
Text Solution
|
- The spring is compressed by a distance a and released. The block again...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks m(1) and m(2) are connected by a spring of force constant K...
Text Solution
|
- एक घर्षणरहित क्षैतिज सतह पर दो द्रव्यमान m(1) तथा m(2) एक स्प्रग से जो...
Text Solution
|
- एक स्प्रिंग के किनारों पर m1" तथा "M2 द्रव्यमान की दो गस्तुएँ जुड़ी ह...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass m(1) and m(2) , resting on a frictionless table, ar...
Text Solution
|