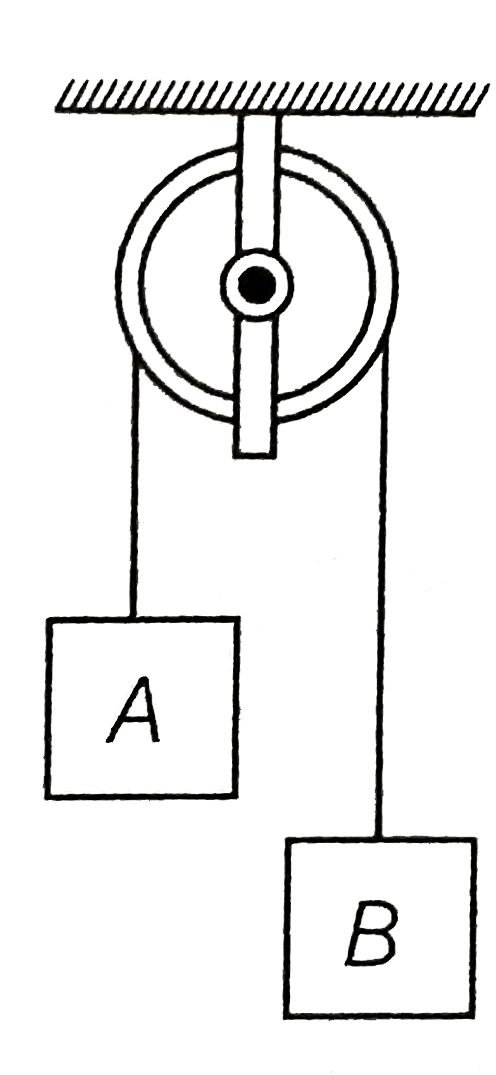Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
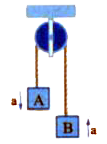
- In the arrangement shown in figure, m(A) = 2kg and m(B) = 1kg. String ...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in Figure, mA=2kg and mB=1kg . String is ligh...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses m(1) and m(2) are in equilibrium. The block m(2) h...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in fig., m(A)=4m, m(B)=3m, and m(c)=8m. Friction i...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in fig., m(A)=4m , m(B)=3m , and m(c)=8m . Frictio...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in fig., m(A)=4m , m(B)=3m , and m(c)=8m . Frictio...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in figure m(B)=4kg , and m(A)=2kg . The pulleys ar...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of masses m(1) and m(2) connected by an inextens...
Text Solution
|
- In terms of masses m(1),m(2) and g, find the acceleration of both the ...
Text Solution
|