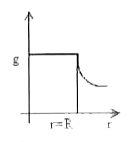
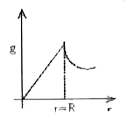
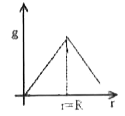
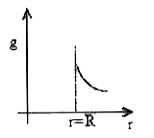
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Assuming the earth to be a uniform sphere of mass M and radium R. whic...
Text Solution
|
- If R= radius of the earth and g= acceleration due to gravity on the su...
Text Solution
|
- If R= radius of the earth and g= acceleration due to gravity on the su...
Text Solution
|
- If earth is assumed to be a sphere of uniform density then plot a grap...
Text Solution
|
- The satellite is moving round the earth (radius of earth = R) at a dis...
Text Solution
|
- Variation of acceleration due to gravity (g) with distance x from the ...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of acceleration due to gravity g with distance d from ce...
Text Solution
|
- Variation of acceleration due to gravity (g) with distance x from the ...
Text Solution
|
- Variation of acceleration due to gravity (g) with distance x from the ...
Text Solution
|