Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
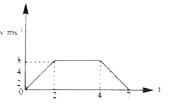
- Figure given here shows the variation of velocity of a particle with t...
Text Solution
|
- Position of a particle at any instant is given by x = 3t^(2)+1 , wher...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of a particle at t=0 "is"vecU = 4hati+3hatj"m"//"sec" and...
Text Solution
|
- If acceleration of particle changing with time is a = (4t-2) m//s^(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- During one dimensional motion on x-axis Velocity time graph for partic...
Text Solution
|
- A particle starts from rest on a straight path, Its acceleration is li...
Text Solution
|
- If displacement S at time t is S=t^(3)-3t^(2)-15t+12, then acceleratio...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity time graph of a body moving in a straight line is shown. ...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration of a particle is given by a = 3t and at t = 0, v = 0,...
Text Solution
|