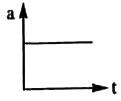
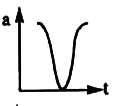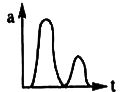A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniformaly moving cricket ball is turned back by hitting it with a b...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform moving cricket ball is turned back by hitting it with a bat ...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150 g is moving with a speed of 12ms^(-1) and i...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150g is moving with a velocity of 12 m/s and is...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with a speed of 12 ms^(-1) is hit ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from an elevator moving upward with acceleration 'a'...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly moving cricket balls is hit with a bat for a very short ti...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 25 g moving with a speed of 12 ms^(-1) is hit b...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly moving cricket balls is hit with a bat for a very short ti...
Text Solution
|