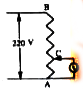Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE-IA|142 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE-IB|71 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise very Short answer type question|15 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) Integer Type Questions|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM-EXERCISE-III
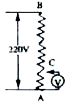
- A potential difference of 220 V is maintained across a 12000 ohm rheos...
Text Solution
|
- A proton, a deuteron and an alpha particle having same momentum enter ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge q moves with a constant velocity v alo...
Text Solution
|
- An electron accelerated through a potential difference V passes throug...
Text Solution
|
- A 2MeV proton is moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 2...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle is accelerated thrught a potential difference of 12...
Text Solution
|
- A charge partilce with velocity V=xhati+yhatj moves in a magnetic fiel...
Text Solution
|
- A parabolic section of wire, as shown in figure is located in the X-Y ...
Text Solution
|
- A semi circular current loop is placed in an uniform magnetic field of...
Text Solution
|
- A straight wire of length 30 cm and mass 60 mg lies in a direction 30^...
Text Solution
|
- A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed po...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the magnetic field at the centre of a current carrying ci...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires A and B are of lengths 40 cm and 30 cm. A is bent into a cir...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of radius 2R is carrying current 'i' . The ratio of ma...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field due to a current carrying circular loop of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- The field due to a wire of n turns and radius r which carries a curren...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is uniformly distributed over the surgace of non conducting...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular coils are made from a uniform copper wire. Radii of circu...
Text Solution
|
- A straight wire is first bent into a circle of radius 'r' and then int...
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire carrying current of 30 A is placed in an exte...
Text Solution
|