Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Exercise (Long Answer Questions)|1 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Exercise (Short Answer Questions)|21 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE EXERCISE (SELF INDUCTANCE AND MUTUAL INDUCTANCE)|12 VideosELECTRIC FIELD AND POTENTIAL
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PROBLEMS (LEVEL-II)|26 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE -II|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Example
- The magnetic flux through a coil perpendicular to its plane is varying...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of 500 turns of wire has an enclosed area of 0.1 m^(2)...
Text Solution
|
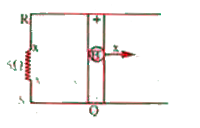
- Figure shows a conducting rod PQ in contact with metal rails RP and SQ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length 21 is bent al mid point so that the angle between two...
Text Solution
|
- A conductor of length 0.1m is moving with a velocity of 4m/ s in a uni...
Text Solution
|
- Find the emf induced across the ends of the conductor shown in the fig...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel rails with negligible resistance are 10.0 cm apart. The a...
Text Solution
|
- A loop ABCD containing two resistors as shown in figure is placed in a...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod MN moves with a speed v parallel to a long straight w...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic bars XX.and YY., of negligible resistan...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass mand length I moves on two frictionless parallel rails i...
Text Solution
|
- A copper rod of length 2m is rotated with a speed of 10 rps, in a unif...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 10cm made up of conducting an non-conducting). The roa...
Text Solution
|
- A copper disc of radius 1 m is rotated about its natural axis with an ...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel with 10 metallic spokes each 0.5 m long is rotated with a spee...
Text Solution
|
- Chaitanya pedals a stationary bicycle at one revolution per second. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A coil of 800 turns and 50 cm^(2) area makes 10 rps about an axis in i...
Text Solution
|
- A magnetic field directed into the page changes with time according to...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field at all points within the cyllindrical region whose ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equivalent resistance between A and B.
Text Solution
|