Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-WAVE MOTION AND SOUND-PROBLEMS (LEVEL - II)
- A railroad train is travelling at 30 m//s in still air. The frequency ...
Text Solution
|
- A railroad train is travelling at 30 m//s in still air. The frequency ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical tuning forks vibrating at the same frequency 256 Hz are ...
Text Solution
|
- Two sound sources are moving in opposite directions with velocities v...
Text Solution
|
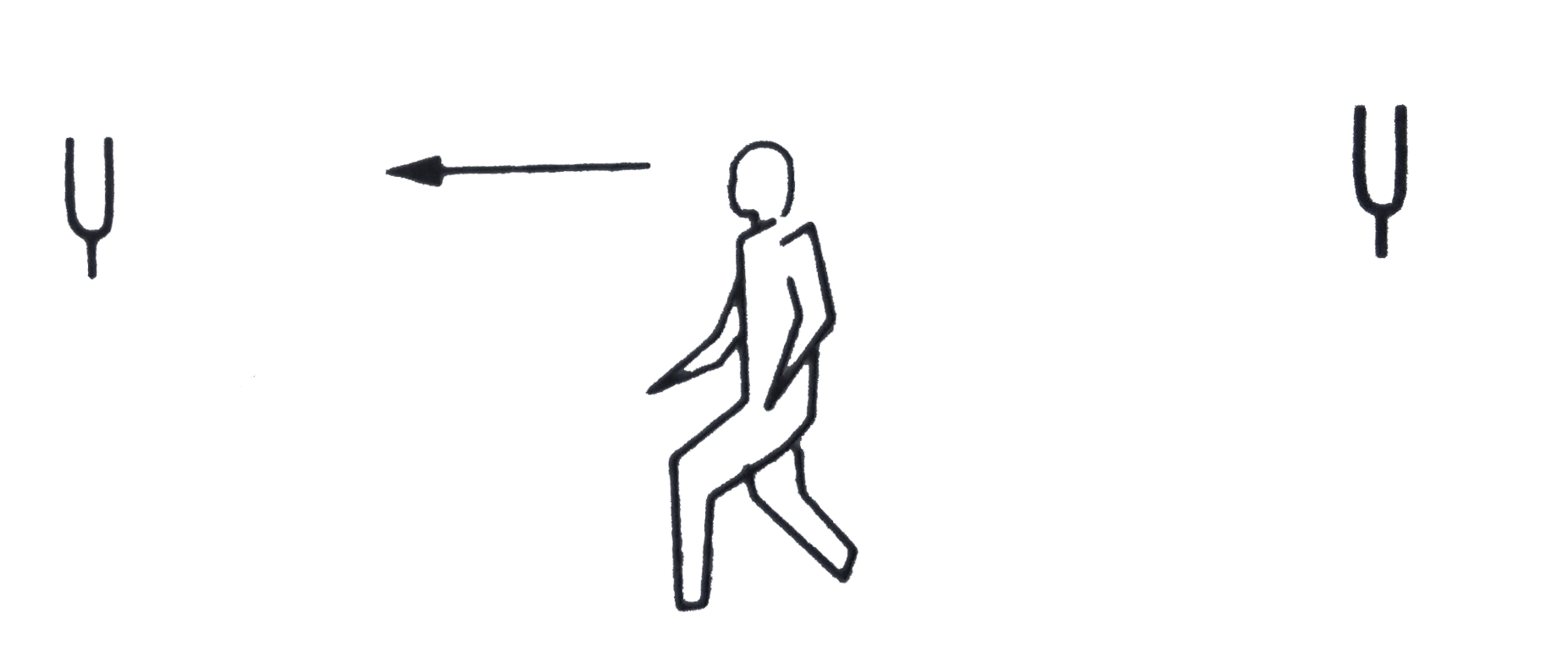
- A 300 Hz source, an observer and wind are moving as shown in the figur...
Text Solution
|
- A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a ca...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary sound sound 's' of frequency 334 Hz and a stationary ovs...
Text Solution
|
- Spherical waves are emitted from a 1.0 W source in an isotropic non-ab...
Text Solution
|
- The intensity of sound from a point source is 1.0 xx 10^-8 Wm^-2, at a...
Text Solution
|
- Most people interpret a 9.0 dB increase in sound intensity level as a ...
Text Solution
|
- About how many times more intense will the normal ear perceiver a soun...
Text Solution
|
- The explosion of a fire cracker in the air at the a heigth of 40 m pro...
Text Solution
|
- The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- If the intensity of sound is doubled, by how many decibels does the so...
Text Solution
|
- Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears painful to a person. A...
Text Solution
|
- Two waves, each having a frequency of 100 Hz and a wavelength of 2.0 c...
Text Solution
|
- Two waves, each having a frequency of 100 Hz and a wavelength of 2.0 c...
Text Solution
|
- Two waves, each having a frequency of 100 Hz and a wavelength of 2.0 c...
Text Solution
|
- Three component sinusoidal waves progressing in the same directions al...
Text Solution
|
- A soldier walks towards a high wall taking 120 steps per minute. When ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.