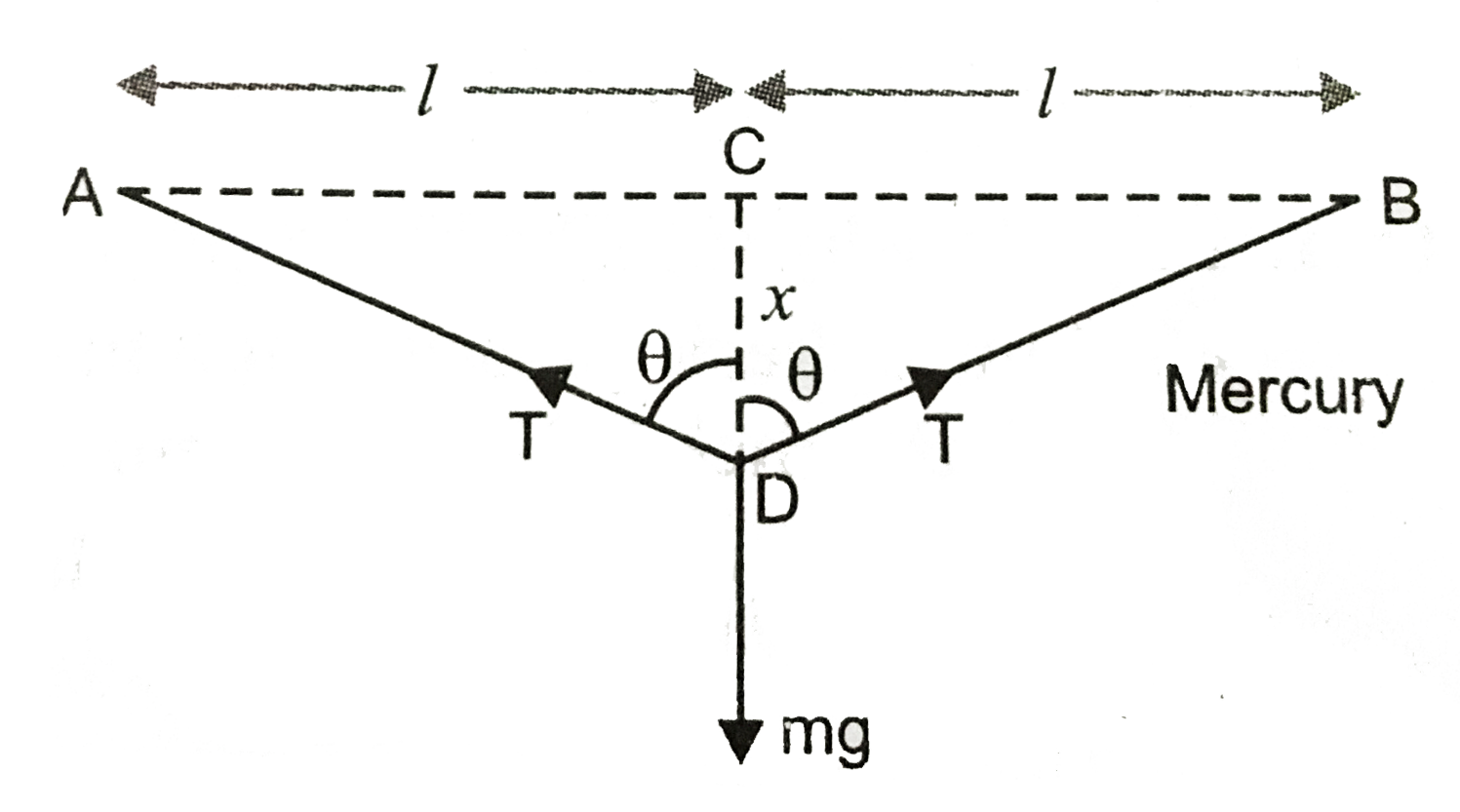
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross-sectional are 0.5 xx 10^(-...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross-sectional are 0.5 xx 10^(-...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0m and cross sectional area 5.0xx10^(-2)...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0m and cross sectional area 2L is streth...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of Length 2L and cross sectional Area A is stretched...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross sectional area 0.50 times ...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross - sectional area 0.50xx10^...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross - sectional area 0.50xx10^...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross - sectional area 0.50xx10^...
Text Solution
|