Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
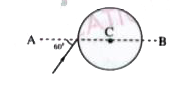
- A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre at C as shwon...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre at C as shown...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light emerges from the opposite surface of the sphe...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes through a transparent sphere of refractive index...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light emerges from the opposite surface of the sphe...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre at C as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Light incidence on a sphere of refractive index sqrt3 placed in a air ...
Text Solution
|
- Parallel rays are incident on a transparent sphere along its one diame...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light is kept on the surface of a sphere and it is f...
Text Solution
|