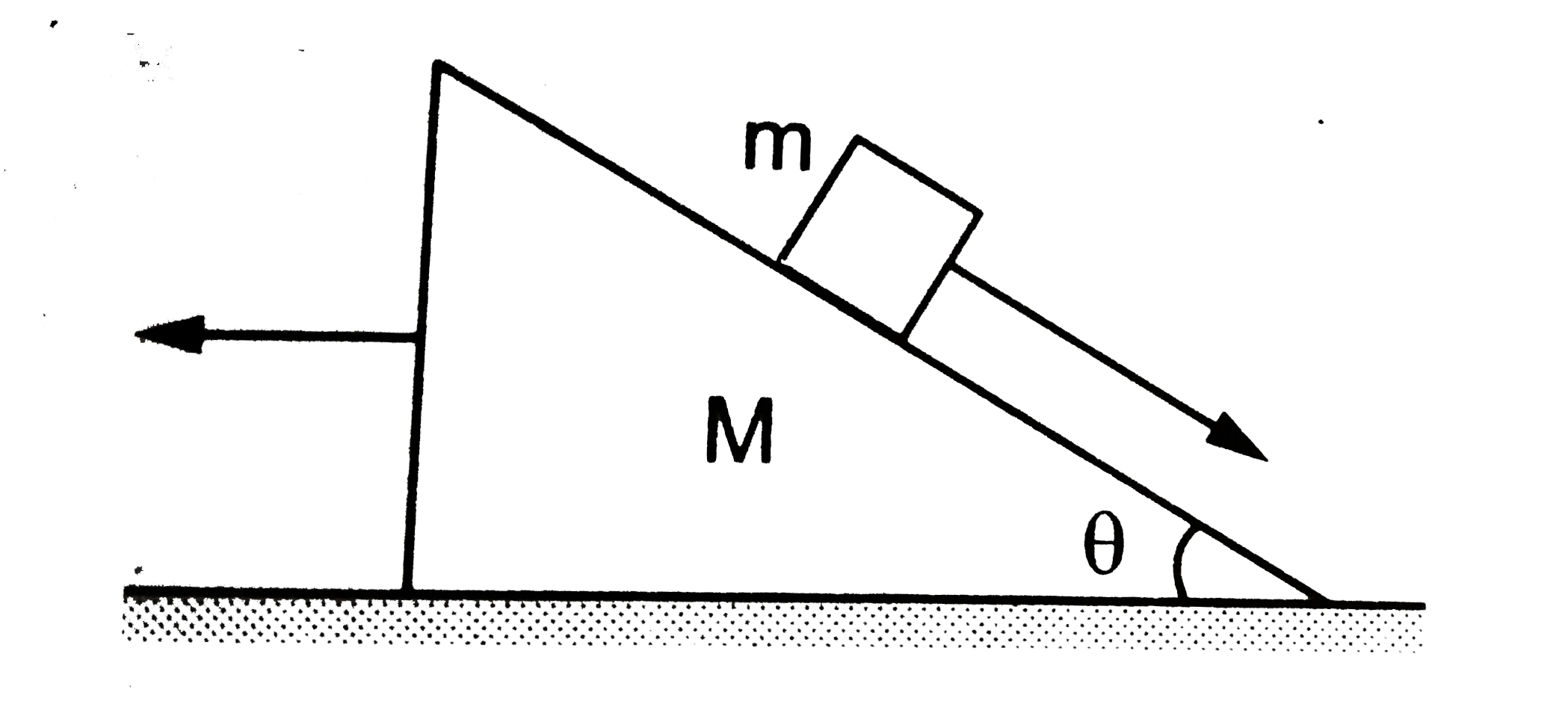
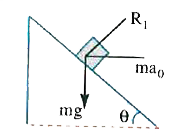
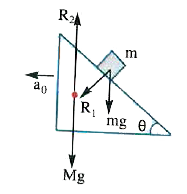
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- All the surfaces shown in figure are assumed to be frictionless. The b...
Text Solution
|
- All the surfaces shownin figure are assumed to be frictionless. The bl...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a small block of mass m which is started with a speed v o...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mas m is placed on a triangular block of mas m, which in tu...
Text Solution
|
- A small block slides with velocity 0.5sqrt(gr) on the horizontal frict...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming all the surfaces to be smooth, find the acceleration of the t...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming all the surface to be frictionless. The smaller block m is m...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a block of mass 2m sliding on a block of mass m. Find the...
Text Solution
|
- A prism of mass M is placed on a horizontal surface. A block of mass m...
Text Solution
|