Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
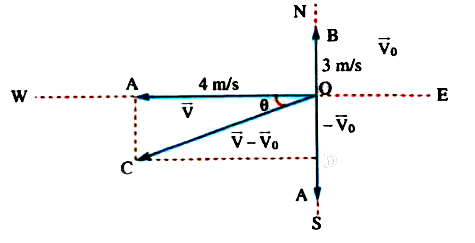
- A body moving in a curved path possesses a velocity 3 m/s towards nort...
Text Solution
|
- A body is moving with velocity 30 m//s towards east. After 10 s its ve...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2 kg is moving with velocity 10 m / s towards east. Ano...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moing with a velocity of 10m//s towards east. After 10s ...
Text Solution
|
- एक कण 5 मीटर/सेकण्ड के वेग से पूरब की ओर जा रहा है । 10 सेकण्ड पश्चात ...
Text Solution
|
- A body moving in a curved path possesses a velocity 3 m/s towards nort...
Text Solution
|
- एक कण पूर्व(E) दिशा की ओर 10 m/s वेग के साथ गति कर रहा है। 10 s पश्चात...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2 kg is moving with velocity 10 m / s towards east. Ano...
Text Solution
|
- A body moving in a curved path possesses a velicty 3m//s towards north...
Text Solution
|