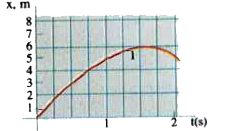
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Find the average velocity for the time intervals Deltat=t(2)-0.75 when...
Text Solution
|
- A cockroach moves rectilinearly such that after sometime t(0) let its ...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of a paticle is given by the equation, v=2t^(2)+5cms^(-1)...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In the upsilon-t diagram as shown in figure, average veloc...
Text Solution
|
- The position of a particle varies with time according to the relation ...
Text Solution
|
- यदि वस्तु समय t(1) तक वेग v(1) से तथा समय t(2) तक वेग v(2) से चले तो...
Text Solution
|
- The average velocity of CO(2) at T(1) K and most probable velocity at ...
Text Solution
|
- एक कण की एक विमा में गति के लिए, कण की स्थिति x और समय t में वक्र चित्...
Text Solution
|
- CO(2) गैस का T(1)K पर औसत वेग (average velocity) तथा T(2)K पर अधितकम प...
Text Solution
|