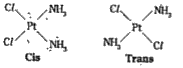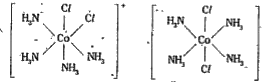Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-MODEL PAPER 1 -SECTION- B
- Derive Bragg's equation .
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the mole fraction of ethylene glycol (C(2)H(6)O(2)) in a sol...
Text Solution
|
- How emulsions are classified ? Give one example for each type of emuls...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following : Zone refining
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following : Poling.
Text Solution
|
- How is ammonia manufactured by Haber's process ? Explain the reactions...
Text Solution
|
- Explain geometrical isomerism in Co-ordination compounds giving suitab...
Text Solution
|
- give the sources of the vitamin and name the disease caused by it di...
Text Solution
|
- Give the sources of the following vitamin and name the diseases cause...
Text Solution
|
- Give the sources of the following vitamins and name the disease caused...
Text Solution
|
- Give the sources of the following vitamins and name the disease caused...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Grignard reagents preparation and application with suitabl...
Text Solution
|