MODERN PUBLICATION-Moment of Inertia-Example
- A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass 10 kg is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclinatio...
Text Solution
|
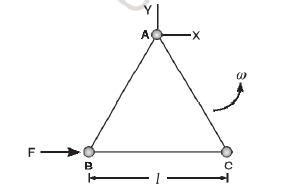
- Three particles A, B and C, each of mass m, are connected to each othe...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles A, B and C, each of mass m, are connected to each othe...
Text Solution
|
- From a circular disc of radius r and mass 9M a small disc of radius r/...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l and mass m is hinged at point O. A small bullet of ...
Text Solution
|
- A homogeneous rod AB of length L= 1.8 m and mass M is pivoted at the c...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar lies on a frictionless horizonta surface and is fre...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere rolls down without slipping from the top of a track in ...
Text Solution
|
- A carpet of mass M made of inextensible material is rolled along its l...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc has radius R and mass m. A particle also of ma...
Text Solution
|
- Define moment of inertia
Text Solution
|
- Is there any difference between moment of inertia and rotational inert...
Text Solution
|
- Why M.I. of called rotational inertia?
Text Solution
|
- Define the term electric dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector qua...
Text Solution
|
- Does M.I. change with change of the axis of rotation?
Text Solution
|
- How does M.I. change with speed of rotation.
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a rigid body, depends upon
Text Solution
|
- What is physical significnce of moment of inertia?
Text Solution
|
- Define radius of gyration.
Text Solution
|