The resultant of two alternating sinusoidal voltages or currents can be found using ___________
a) Triangular law
b) Parallelogram law
c) Either triangular or parallelogram law
d) Neither triangular nor parallelogram law
The resultant of two alternating sinusoidal voltages or currents can be found using ___________
a) Triangular law
b) Parallelogram law
c) Either triangular or parallelogram law
d) Neither triangular nor parallelogram law
a) Triangular law
b) Parallelogram law
c) Either triangular or parallelogram law
d) Neither triangular nor parallelogram law
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
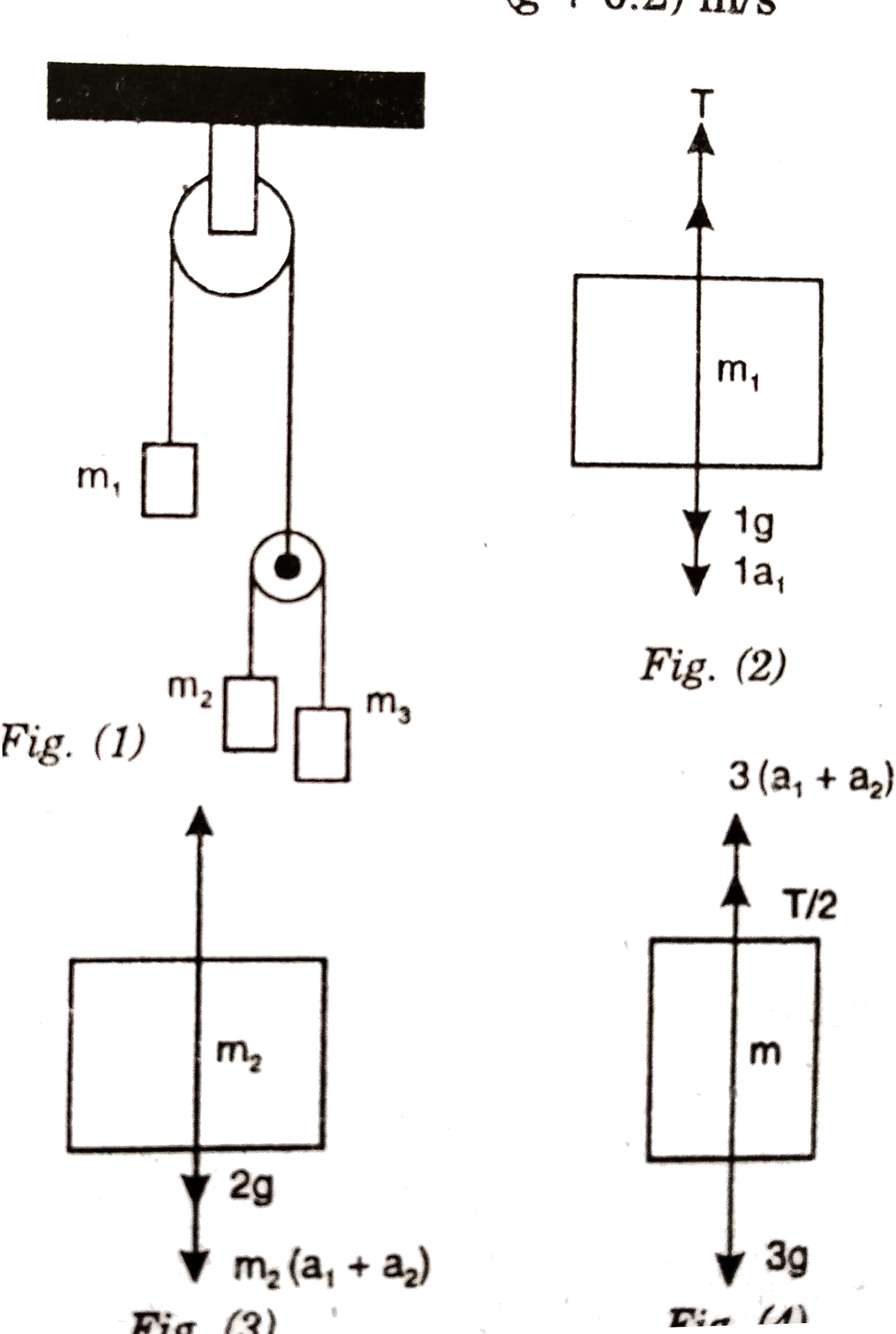
Let the block `m_1` moves upward with accelerastion `a_1 ` and the two block `m_2 and m_3` have relative cceleration `a_2` due to the diffference of weight between them,
So, the actual acceleratin of the blocks `m_1 , m_2 and m_3` will be `a_1(a_1-a_2) and (a_1+a_2)` as shown
From ure 2, `T-1g-1a_2=0`....i.
From ure 3, `
` T/2 -2 g-2(a_1-a_2)=0` ........ii. `
From ure 4,
` T/2 -3g-3(a_1+a_2)=0` ........iii.
From equations I. and ii. elimiN/Ating T, we get,
`1g+1a_2=4g+4(a_1+a_2)`
`rarr 5a_2-4a_1=3g` ...........iv.
From equations ii and iii we get
` 2g+2(a_1-a_2)=3-3(a_1-a_2)`
`rarr 5a_1 +a_2=g` .........v.
Solving equations iv and v we get,
` a_1 = 2g/29`
`and a_2 =g-5a_1`
`= g-(10g)/29=(19g)/29`
So, `a_1 -a_2= (2g)/(17g)/29`
and `a_1+a_2 =(2g)/29+(19g)/29=(21g)/29`
So, acceleratiion of `m_1, m_2 and m_3` are ` `(19g)/29 (up) , (17g)/29` (down) and `(21g)/29 (down), respectively.
Again, from `u=0, S=20 cm= 0.2 cm and
` a_2= (19g)/29 [g=10 m/s^2]`
:. S=ut+1/2 at^2`
`rarr 0.2=1/2xx19/29gt^2`
` rarr t=0.25 sec` .
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
For each of the following, draw a circle and inscribe the figure given. If a polygon of the given type can’t be inscribed, write not possible. (a) Rectangle (b)Trapezium (c) Obtuse triangle (d) Non-rectangular parallelogram (e) Accute isosceles triangle
Assertion: A vector quantity is a quantity that has both magnitude and a direction and obeys the triangle law of addition or equivalent the parallelogram law of addition. Reason: The magnitude of the resultant vector of two given vectors can never be less than the magnitude of any of the given vector.
In parallelogram ABCD, the ratio /_A: /_B:/_C:/_D can be……..
Use Lenz's law to determine the direction of induced current in the situations described by figure. (a) A wire of irregular shape turning into a circular shape, (b) A circular loop being deformed into a narrow straight wire.
The lens governing the behavior of the rays namely rectilinear propagation laws of reflection and refraction can be summarised in one fundamental law known as Fermat's principle. According to this principle a ray of light travels from one point to another such that the time taken is at a stationary value (maximum or minimum). if c is the velocity of light in a vacuum the velocity in a medium of refractive index mu is (c)/(mu) hence time taken to travel a distance l is (mul)/(c) if the light passes through a number of media, the total time taken is ((1)/(c))summul or (1)/(c)intmudl if refractive index varies continuously. Now summul is the total path, so that fermat's principle states that the path of a ray is such that the optical path in at a stationary value. this principle is obviously in agreement with the fact that the ray are straight lines i a homogenous isotropic medium. it is found that it also agrees with the classical laws of reflection and refraction. Q. The optical length followed by ray from point A to B given that laws of reflection are obeyed as shown in figure is
The lens governing the behavior of the rays namely rectilinear propagation laws of reflection and refraction can be summarised in one fundamental law known as Fermat's principle. According to this principle a ray of light travels from one point to another such that the time taken is at a stationary value (maximum or minimum). if c is the velocity of light in a vacuum the velocity in a medium of refractive index mu is (c)/(mu) hence time taken to travel a distance l is (mul)/(c) if the light passes through a number of media, the total time taken is ((1)/(c))summul or (1)/(c)intmudl if refractive index varies continuously. Now summul is the total path, so that fermat's principle states that the path of a ray is such that the optical path in at a stationary value. this principle is obviously in agreement with the fact that the ray are straight lines i a homogenous isotropic medium. it is found that it also agrees with the classical laws of reflection and refraction. Q. The optical path length followed by ray from point A to B given that laws of refraction are obeyed as shown in figure.
The lens governing the behavior of the rays namely rectilinear propagation laws of reflection and refraction can be summarised in one fundamental law known as Fermat's principle. According to this principle a ray of light travels from one point to another such that the time taken is at a stationary value (maximum or minimum). if c is the velocity of light in a vacuum the velocity in a medium of refractive index mu is (c)/(mu) hence time taken to travel a distance l is (mul)/(c) if the light passes through a number of media, the total time taken is ((1)/(c))summul or (1)/(c)intmudl if refractive index varies continuously. Now summul is the total path, so that fermat's principle states that the path of a ray is such that the optical path in at a stationary value. this principle is obviously in agreement with the fact that the ray are straight lines i a homogenous isotropic medium. it is found that it also agrees with the classical laws of reflection and refraction. Q. If refractive index of a slab varies as mu=1+x^(2) where x is measured from one end then optical path length of a slab of thickness 1 m is
An experimental setup of verification of photoelectric effect is shown in the diagram. The voltage across the electrode is measured with the help of an ideal voltmetar, and which can be varied by moving jockey 'J' on the potentiometer wire. The battery used in potentiometer circuit is of 20 V and its internal resistance is 2omega . The resistance of 100 cm long potentiometer wire is 8 omega . The photo current is measured with the help of an ideal ammeter. Two plates of potassium oxide of area 50 cm^(2) at separation 0.5 mm are used in the vacuum tube. Photo current in the circuit is very small so we can treat potentiometer circuit an indepdent circuit. The wavelength of various colours is as follows : |{:("Light",underset("Violet")(1),underset("Blue")(2),underset("Green")(3),underset("Yellow")(4),underset("Orange")(5),underset("Red")(6)),(lambda "in" Årarr,4000-4500,4500-5000,5000-5500,5500-6000,6000-6500,6500-7000):}| When radiation falls on the cathode plate a current of 2muA is recorded in the ammeter. Assuming that the vecuum tube setup follows ohm's law, the equivalent resistance of vacuum tube operating in this case when jockey is at end P.
Figure shows the relationship between tensile stress and strain for a typical material. Below proportional point A, stress is directly proportional to strain which means Young's moudulus (Y) is a constant. In this region the material obeys Hooke's law. Provided the strain is below the yield point 'B' the material returns to its original shape and size when the force is removed. Beyond the yield point, the material retains a permancnt deformation after the stress is removed. For stresses beyond the yeld point, the material exhibit plastic flow, which means that it continues to elongate for little increases in the stress. Beyond C a local constriction occurs. The material fractures at D (i.e. breaking point). The graph below shows the stress-strain curve for 4 different materials. If you bough a new shoe which bites in the beginning and later on fits perfectly, then the material used to making the shoe is
Recommended Questions
- The resultant of two alternating sinusoidal voltages or currents can b...
Text Solution
|
- Parallelogram law of addition of vectors
Text Solution
|
- Parallelogram Law Of Addition Of Vectors
Text Solution
|
- Parallelogram law of vectors is applicable to the addition of :
Text Solution
|
- Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
Text Solution
|
- In parallelogram law of vector, the direction of resultant vector is g...
Text Solution
|
- Explain in detail the triangle law of addition.
Text Solution
|
- Explain in detail the triangle law of addition.
Text Solution
|
- State the law of parallelogram of addition of two vectors ?
Text Solution
|