A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Consider the situation shown in figure. The wall is smooth but the sur...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure. The wall is smooth but the sur...
Text Solution
|
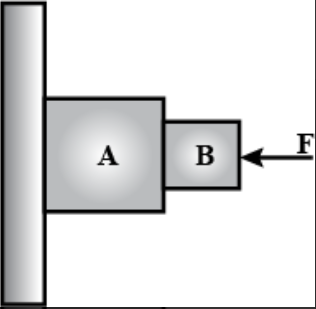
- Figure shows two block A and B pushed against the wall with the force ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the system as shown. The wall is smooth, but the surface of b...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the system shown in the figure. The wall is smmoth, but the s...
Text Solution
|
- The system is pushed by a force F as shown in figure. All surfaces are...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wall is smooth but the...
Text Solution
|
- If the system is in equilibrium, the magnitude of friction acting on b...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wall is smooth but the...
Text Solution
|