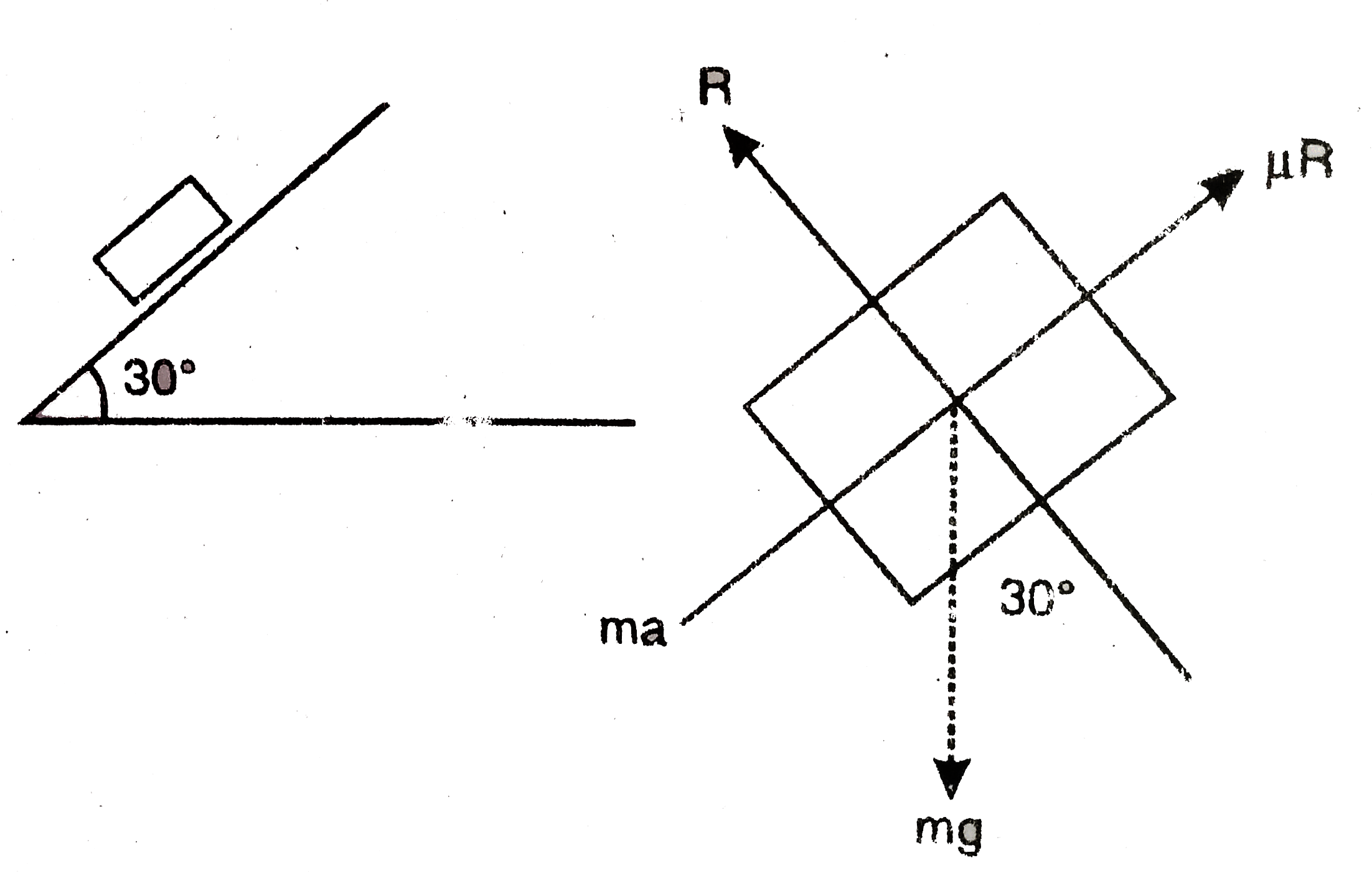
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A block slides down an inclined surface of inclination 30^0 with the h...
Text Solution
|
- A block slides down an inclined surface of inclination 30^0 with the h...
Text Solution
|
- A block slides down an incline of angle 30^(@) with an acceleration of...
Text Solution
|
- A block slides down an incline of 30^(@) with the horizontal starting ...
Text Solution
|
- A block is at rest on an inclined plane making an angle alpha with the...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m rests on a rough inclined plane. The coefficient of ...
Text Solution
|
- A block starting from rest slides down a rough fixed incline having an...
Text Solution
|
- 30^(@) झुकाव वाले एक आनत तल पर एक गुटके को फिसलने के लिए छोड़ दिया जात...
Text Solution
|
- क्षैतिज से 30^(@) झुकाव वाले आनत तल पर एक गुटका नीचे की और फिसलता है...
Text Solution
|