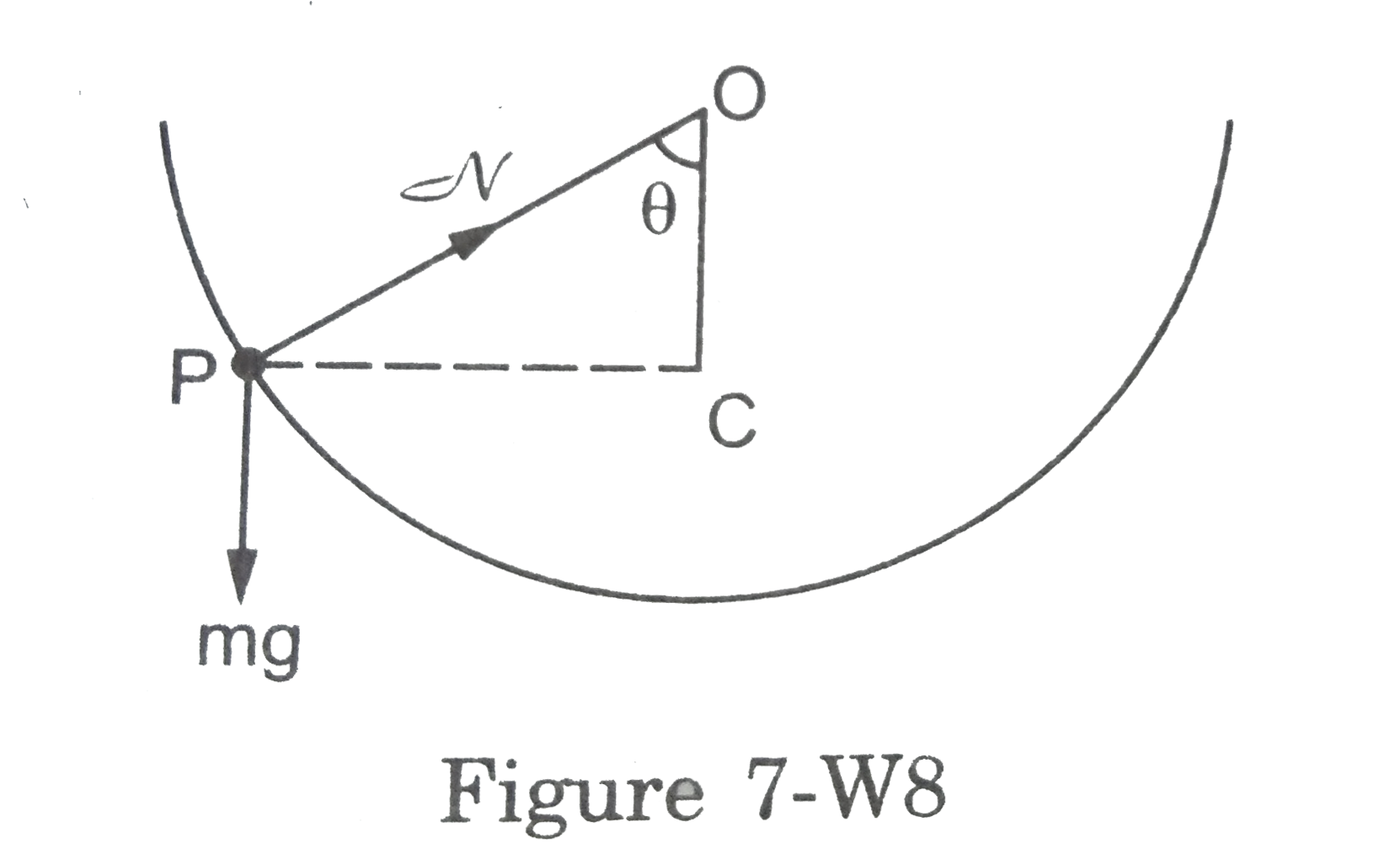
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl is made of steel, 0.25 cm thick. The inner radiu...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A hemisphericla bowl of rdius R is rotated about its axis of symetry w...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A block is kept inside a hemispherical bowl rotating with angular velo...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius r is rotated with an angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|
- A hemispherical bowl of radius R is set rotating about its axis of sym...
Text Solution
|