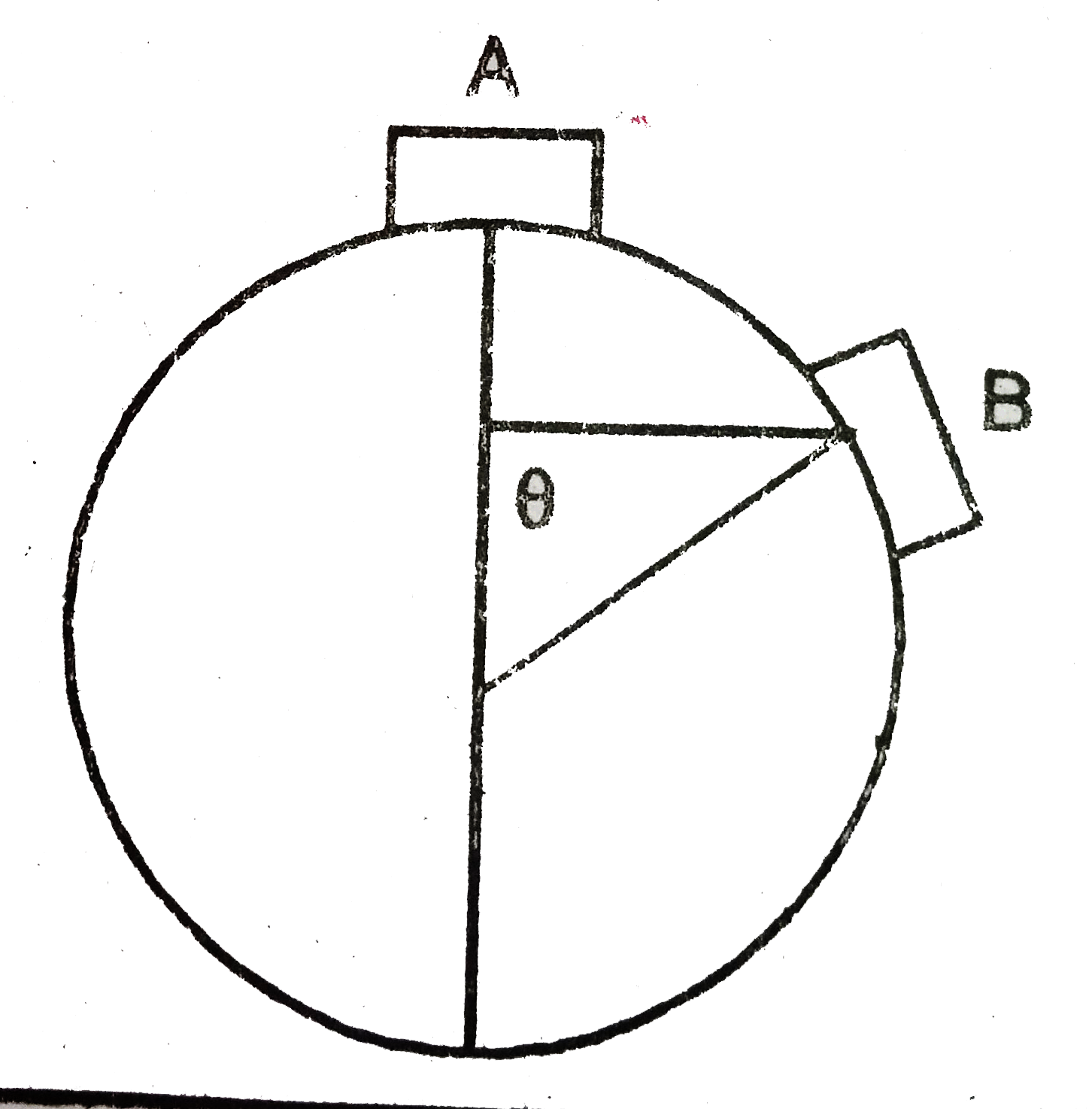
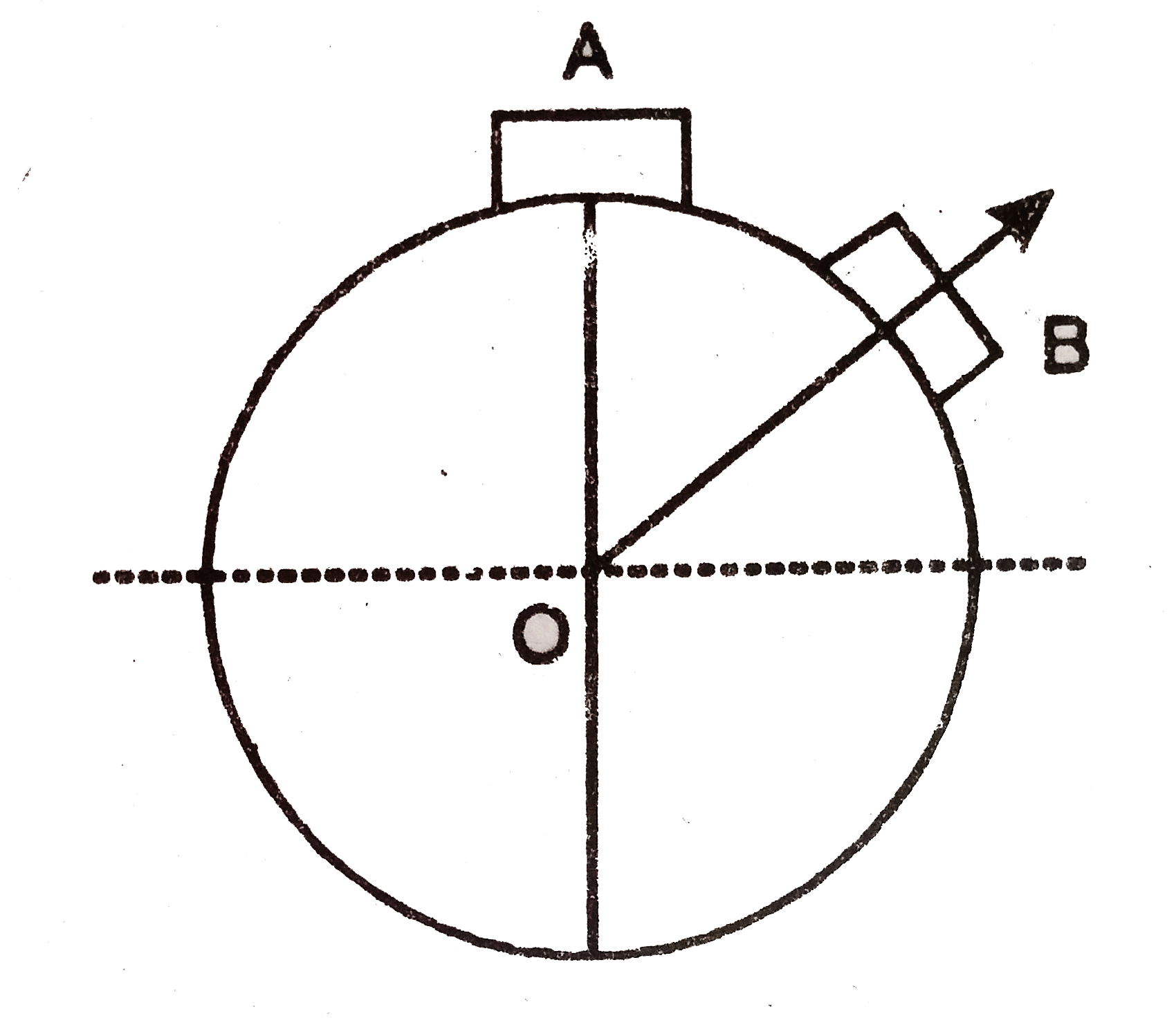
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting fro...
Text Solution
|
- A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting fro...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with velocity u horizontally from the top of a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m starts to slide down from the top of the fixed sm...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is released on a fixed. Smooth sphere of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- A Particle is kept at rest at the top of a sphere of diameter 42m.when...
Text Solution
|
- Particle slides down the surface of a smooth fixed sphere of radius r ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m being to slide down a fixed smooth sphere from th...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m begins to slide down on a fixed smooth sphere fro...
Text Solution
|