A smooth spehre of radius R is made to translate oin a straight line with a constant acceleration a. A particle kept on the top of the sphere is released rom there at zero velocity with respect to the sphere. Find the speed of the particle with respect to the sphere as a functon of the angle `theta` it slides.
A smooth spehre of radius R is made to translate oin a straight line with a constant acceleration a. A particle kept on the top of the sphere is released rom there at zero velocity with respect to the sphere. Find the speed of the particle with respect to the sphere as a functon of the angle `theta` it slides.
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
A, B, C
Let the spehere moves towards left with an accelertion a.
Let m=mass of the particle
The particle m will also experience the inertia due to acceleratioiN/A as it is in the sphere. It will also experience the tangential inertia force `[m((dv)/(dt)] and centrifugal force ((mv^2)/R)`.
for the free body diagram
`m(dv)/(dt)=macostheta+mgsintheta`
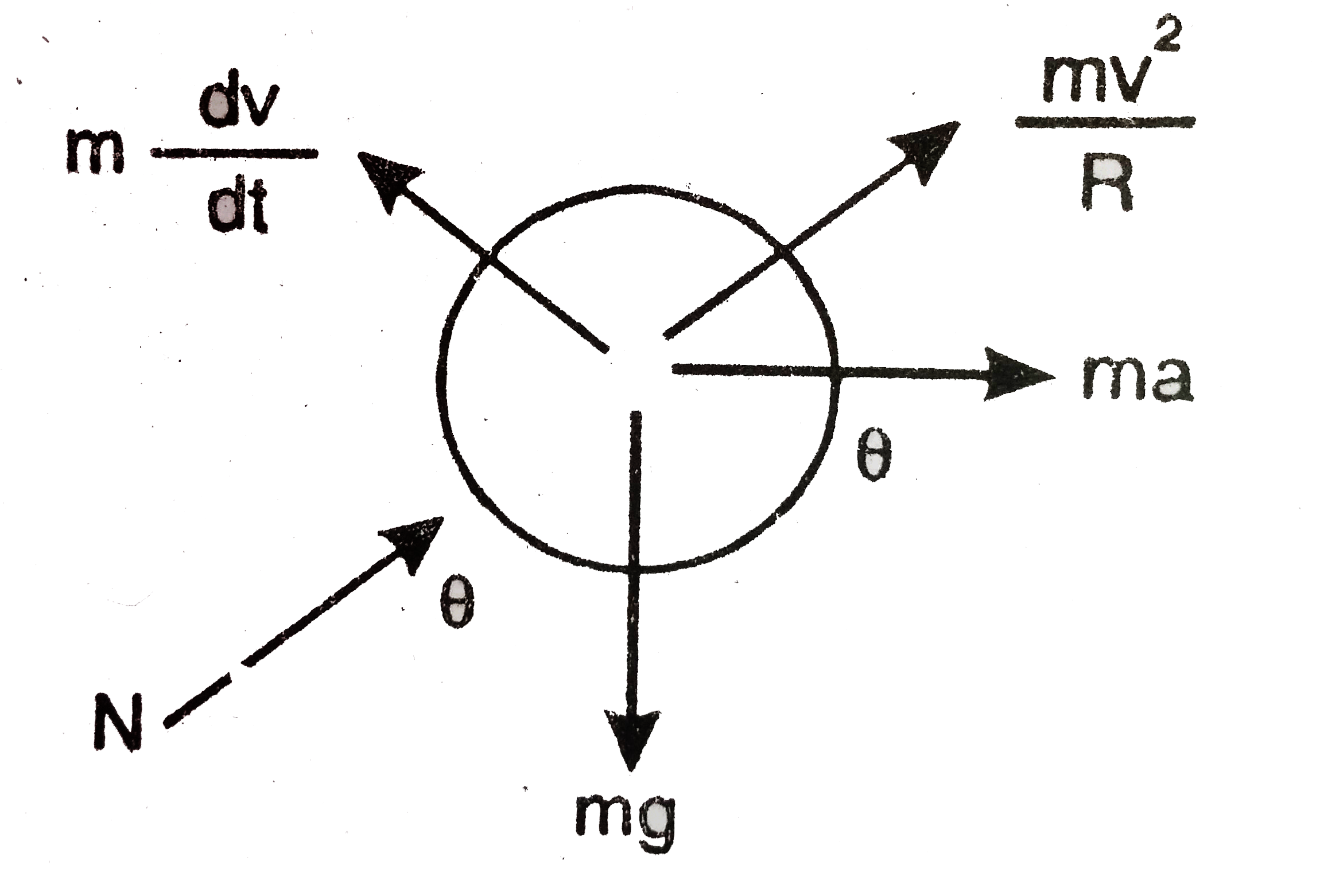
`rarr mv(dv)/(dt)`
`=ma.costheta(R(dtheta)/(dt)+mgsintheta(R(dtheta)/(dt))` (beause v=R (dtheta)/(dt)`
`v dv =a R costheta dtheta+gRsinthetadtheta`
`v^2/2=aRsintheta-gRcostheta+C`
givin that at `theta=0, v=0`
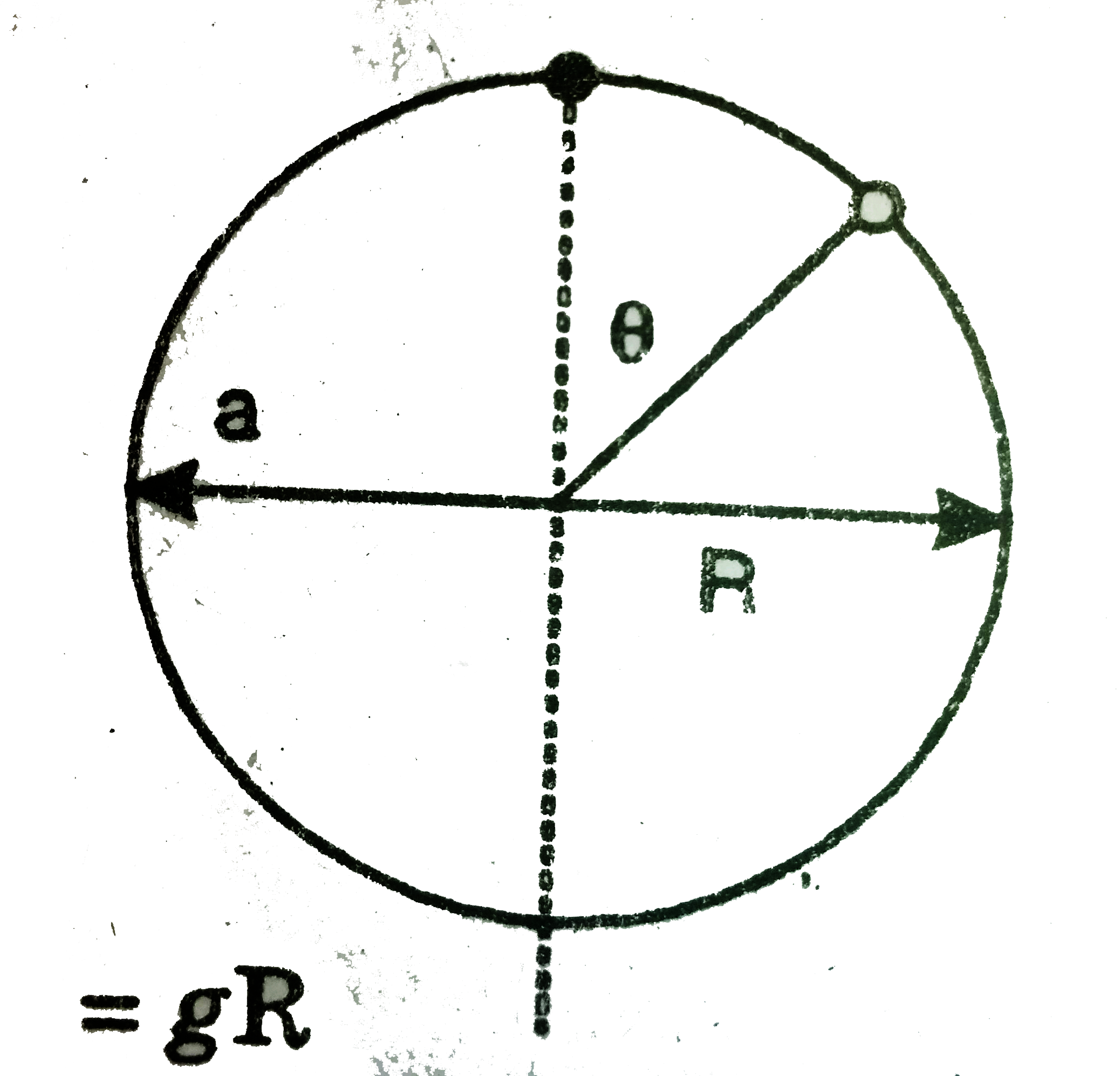
So, C=gR
`rarr v^2/2=aRsintheta-gRcostheta+gR`
`rarr v^2=2R(asintheta)+g-gcostheta)`
`rarr v=[2R(asintheta+g-gcostheta)]^(1/2)`
Let m=mass of the particle
The particle m will also experience the inertia due to acceleratioiN/A as it is in the sphere. It will also experience the tangential inertia force `[m((dv)/(dt)] and centrifugal force ((mv^2)/R)`.
for the free body diagram
`m(dv)/(dt)=macostheta+mgsintheta`

`rarr mv(dv)/(dt)`
`=ma.costheta(R(dtheta)/(dt)+mgsintheta(R(dtheta)/(dt))` (beause v=R (dtheta)/(dt)`
`v dv =a R costheta dtheta+gRsinthetadtheta`
`v^2/2=aRsintheta-gRcostheta+C`
givin that at `theta=0, v=0`

So, C=gR
`rarr v^2/2=aRsintheta-gRcostheta+gR`
`rarr v^2=2R(asintheta)+g-gcostheta)`
`rarr v=[2R(asintheta+g-gcostheta)]^(1/2)`
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A hemisphere of radius R and mass 4 m is free to slide with its base on a smooth horizontal table . A particle of mass m is placed on the top of the hemisphere . The angular velocity of the particle relative to centre of hemisphere at an angular displacement theta when velocity of hemisphere has become v is
A large , heavy box is sliding without friction down a smooth plane of inclination theta . From a point P on the bottom of the box , a particle is projected inside the box . The initial speed of the particle with respect to the box is u , and the direction of projection makes an angle alpha with the bottom as shown in Figure . (a) Find the distance along the bottom of the box between the point of projection p and the point Q where the particle lands . ( Assume that the particle does not hit any other surface of the box . Neglect air resistance .) (b) If the horizontal displacement of the particle as seen by an observer on the ground is zero , find the speed of the box with respect to the ground at the instant when particle was projected .
An accelration produces a narrow beam of protons, each having an initial speed of v_(0) . The beam is directed towards an initially uncharges distant metal sphere of radius R and centered at point O. The initial path of the beam is parallel to the axis of the sphere at a distance of (R//2) from the axis, as indicated in the diagram. The protons in the beam that collide with the sphere will cause it to becomes charged. The subsequentpotential field at the accelerator due to the sphere can be neglected. The angular momentum of a particle is defined in a similar way to the moment of a force. It is defined as the moment of its linear momentum, linear replacing the force. We may assume the angular momentum of a proton about point O to be conserved. Assume the mass of the proton as m_(P) and the charge on it as e. Given that the potential of the sphere increases with time and eventually reaches a constant velue. One the potential of the sphere has reached its final, constant value, the minimum speed v of a proton along its trajectory path is given by
An accelration produces a narrow beam of protons, each having an initial speed of v_(0) . The beam is directed towards an initially uncharges distant metal sphere of radius R and centered at point O. The initial path of the beam is parallel to the axis of the sphere at a distance of (R//2) from the axis, as indicated in the diagram. The protons in the beam that collide with the sphere will cause it to becomes charged. The subsequentpotential field at the accelerator due to the sphere can be neglected. The angular momentum of a particle is defined in a similar way to the moment of a force. It is defined as the moment of its linear momentum, linear replacing the force. We may assume the angular momentum of a proton about point O to be conserved. Assume the mass of the proton as m_(P) and the charge on it as e. Given that the potential of the sphere increases with time and eventually reaches a constant velue. After a long time, when the potential of the sphere reaches a constant value, the trajectory of proton is correctly sketched as
An accelration produces a narrow beam of protons, each having an initial speed of v_(0) . The beam is directed towards an initially uncharges distant metal sphere of radius R and centered at point O. The initial path of the beam is parallel to the axis of the sphere at a distance of (R//2) from the axis, as indicated in the diagram. The protons in the beam that collide with the sphere will cause it to becomes charged. The subsequentpotential field at the accelerator due to the sphere can be neglected. The angular momentum of a particle is defined in a similar way to the moment of a force. It is defined as the moment of its linear momentum, linear replacing the force. We may assume the angular momentum of a proton about point O to be conserved. Assume the mass of the proton as m_(P) and the charge on it as e. Given that the potential of the sphere increases with time and eventually reaches a constant velue. The limiting electric potential of the sphere is
An accelration produces a narrow beam of protons, each having an initial speed of v_(0) . The beam is directed towards an initially uncharges distant metal sphere of radius R and centered at point O. The initial path of the beam is parallel to the axis of the sphere at a distance of (R//2) from the axis, as indicated in the diagram. The protons in the beam that collide with the sphere will cause it to becomes charged. The subsequentpotential field at the accelerator due to the sphere can be neglected. The angular momentum of a particle is defined in a similar way to the moment of a force. It is defined as the moment of its linear momentum, linear replacing the force. We may assume the angular momentum of a proton about point O to be conserved. Assume the mass of the proton as m_(P) and the charge on it as e. Given that the potential of the sphere increases with time and eventually reaches a constant velue. If the initial kinetic energy of a proton is 2.56 ke V , then the final potential of the sphere is
An accelration produces a narrow beam of protons, each having an initial speed of v_(0) . The beam is directed towards an initially uncharges distant metal sphere of radius R and centered at point O. The initial path of the beam is parallel to the axis of the sphere at a distance of (R//2) from the axis, as indicated in the diagram. The protons in the beam that collide with the sphere will cause it to becomes charged. The subsequentpotential field at the accelerator due to the sphere can be neglected. The angular momentum of a particle is defined in a similar way to the moment of a force. It is defined as the moment of its linear momentum, linear replacing the force. We may assume the angular momentum of a proton about point O to be conserved. Assume the mass of the proton as m_(P) and the charge on it as e. Given that the potential of the sphere increases with time and eventually reaches a constant velue. The total energy (E) of a proton in the beam travelling with seed v at a distance of r (r ge R) from point O. Assuming that the sphere has acquired an electrostatic charge Q is
A cavity of radius R//2 is made inside a solid sphere of radius R . The centre of the cavity is located at a distance R//2 from the centre of the sphere. The gravitational force on a particle of a mass 'm' at a distance R//2 from the centre of the sphere on the line joining both the centres of sphere and cavity is (opposite to the centre of cavity). [Here g=GM//R^(2) , where M is the mass of the solide sphere]
On a frictionless horizontal surface , assumed to be the x-y plane , a small trolley A is moving along a straight line parallel to the y-axis ( see figure) with a constant velocity of (sqrt(3)-1) m//s . At a particular instant , when the line OA makes an angle of 45(@) with the x - axis , a ball is thrown along the surface from the origin O . Its velocity makes an angle phi with the x -axis and it hits the trolley . (a) The motion of the ball is observed from the frame of the trolley . Calculate the angle theta made by the velocity vector of the ball with the x-axis in this frame . (b) Find the speed of the ball with respect to the surface , if phi = (4 theta )//(4) .
A small sphere of radius R is held against the inner surface of a larger sphere of radius 6R. The masses of large and small spheres are 4M and M, respectively , this arrangement is placed on a horizontal table. There is no friction between any surfaces of contact. The small sphere is now released. Find the coordinates of the centre of the larger sphere when the smaller sphere reaches the other extreme position.
Recommended Questions
- A smooth spehre of radius R is made to translate oin a straight line w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting fro...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth spehre of radius R is made to translate oin a straight line w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle rests on the top of a smooth hemisphere of radius r . It is...
Text Solution
|
- A small body A starts sliding off the top of a smooth sphere of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth spehre of radius R is made to translate oin a straight line w...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth sphere of radius R is moving in a straight line with an accel...
Text Solution
|
- R त्रिज्या के एक स्थिर एंव चिकने गोले पर m द्रव्यमान का एक कण पकड़कर र...
Text Solution
|
- R त्रिज्या के एक स्थिर एंव चिकने गोले पर m द्रव्यमान का एक कण पकड़कर र...
Text Solution
|