Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
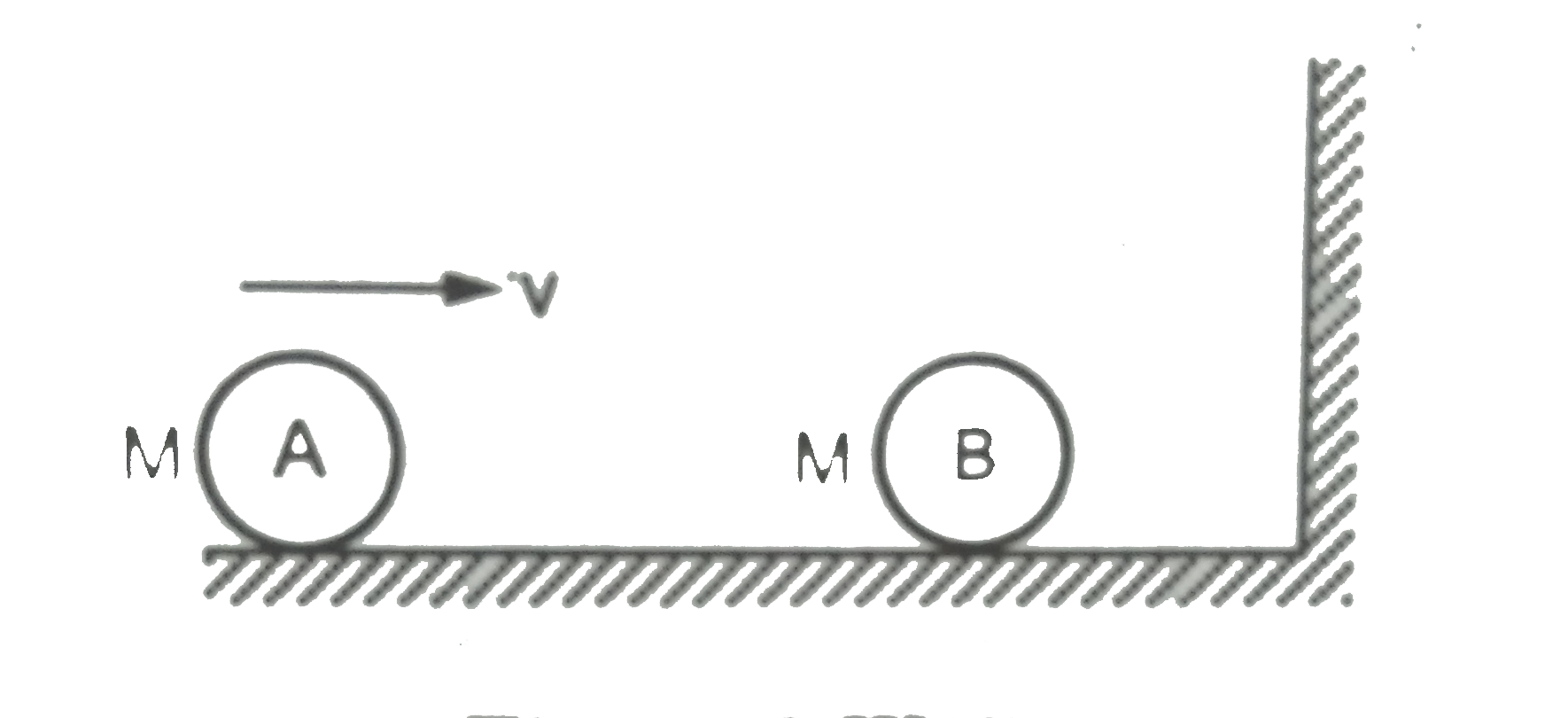
- The two balls shwonin figure are indentical the first moving at a spee...
Text Solution
|
- The two balls shown in figure are identical the first moving at a spee...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is moving with velocity 2m//s towards a heavy wall moving towar...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy ball moving with speed v collides with a tiny ball. The collis...
Text Solution
|
- A highly elastic ball moving at a speed of 3 m//s approaches a wall mo...
Text Solution
|
- A ball moving on a horizontal frictionless plane hits an identical bal...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls each of mass 'm' are moving with same velocity v on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with speed v towards the right strikes a wall ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball moving with speed u collides with an identical ball at rest. Th...
Text Solution
|