Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
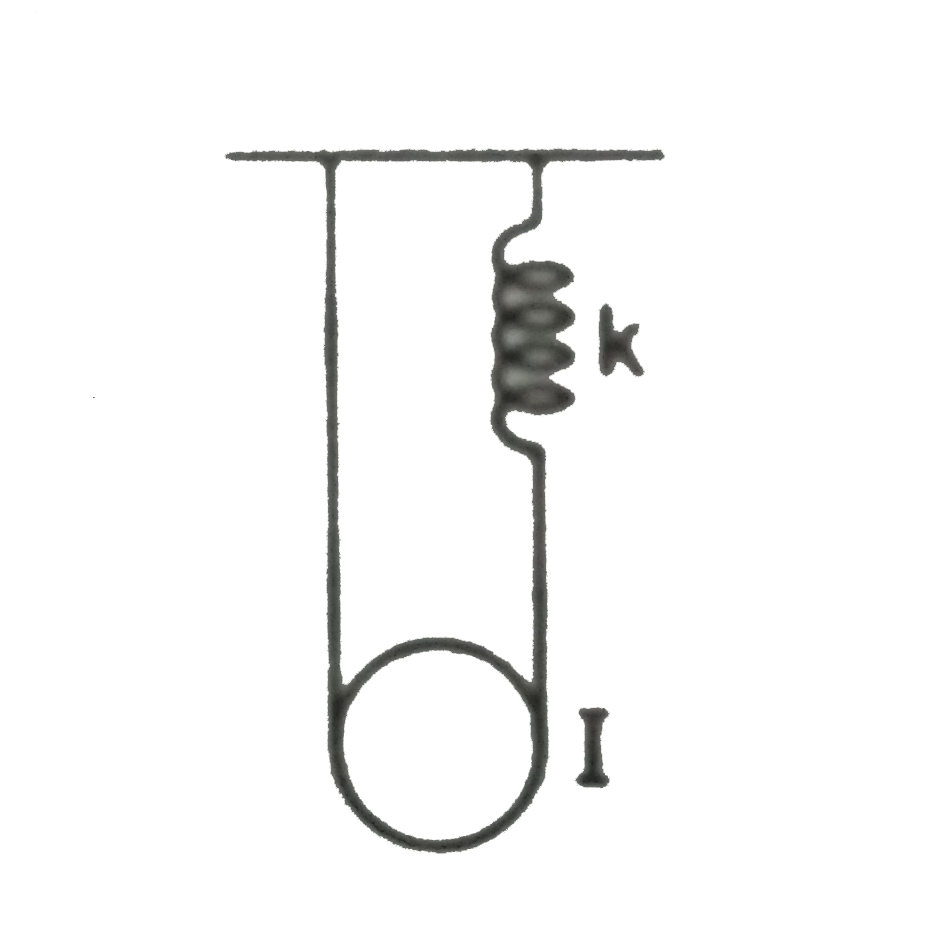
- The pulley shown in figure has a moment of inertias I about its xis an...
Text Solution
|
- The pulley shown in figure has a moment of inertia I about it's axis a...
Text Solution
|
- The pulley shown in figure has a moment of inertias I about its xis an...
Text Solution
|
- Solve the previous problem if the pulley has a moment of inertia I abo...
Text Solution
|
- Find the frequency of small oscillations of the arrangement illustrate...
Text Solution
|
- An arrangement of spring , strings, pulley and masses is shown in the ...
Text Solution
|
- दो द्रव्यमान तथा M एक घिरनी पर से होकर गुजर रही एक रस्सी से जुड़ हुए ह...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a system consisting of pulley having radius R, a spring o...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in the figure. A mass is hanging from a i...
Text Solution
|