Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
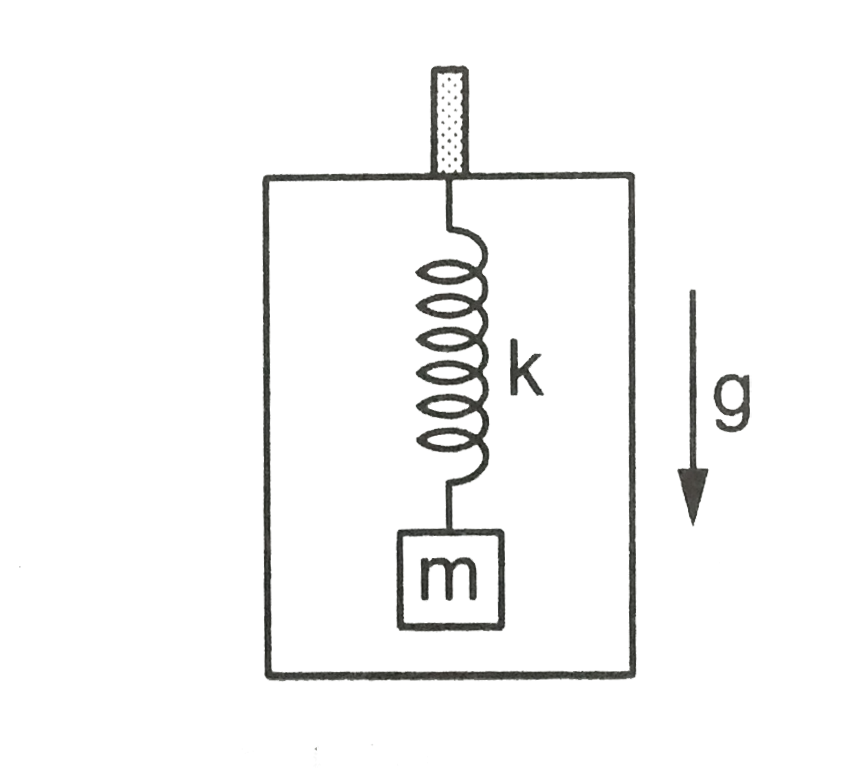
- A block of mass m is suspended from the ceiling of a stationary standi...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is suspended from the ceiling of a stationary standi...
Text Solution
|
- A spring mass system is hanging from the celling of an elevator in equ...
Text Solution
|
- A spring mass system is hanging from the ceiling of an elevator in equ...
Text Solution
|
- A spring mass system is hanging from the ceiling of an elevator in equ...
Text Solution
|
- An engineer is designing a spring to be placed at the bottom of an ele...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m suspended from a spring of spring constant k. Find t...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान का एक पिंड स्प्रिंग नियताक वाले एक स्प्रिग के एक सिरे से बंध...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 20 g connected to a spring of spring constant k, execut...
Text Solution
|