Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ELECTRIC FIELD AND POTENTIAL-Exercises
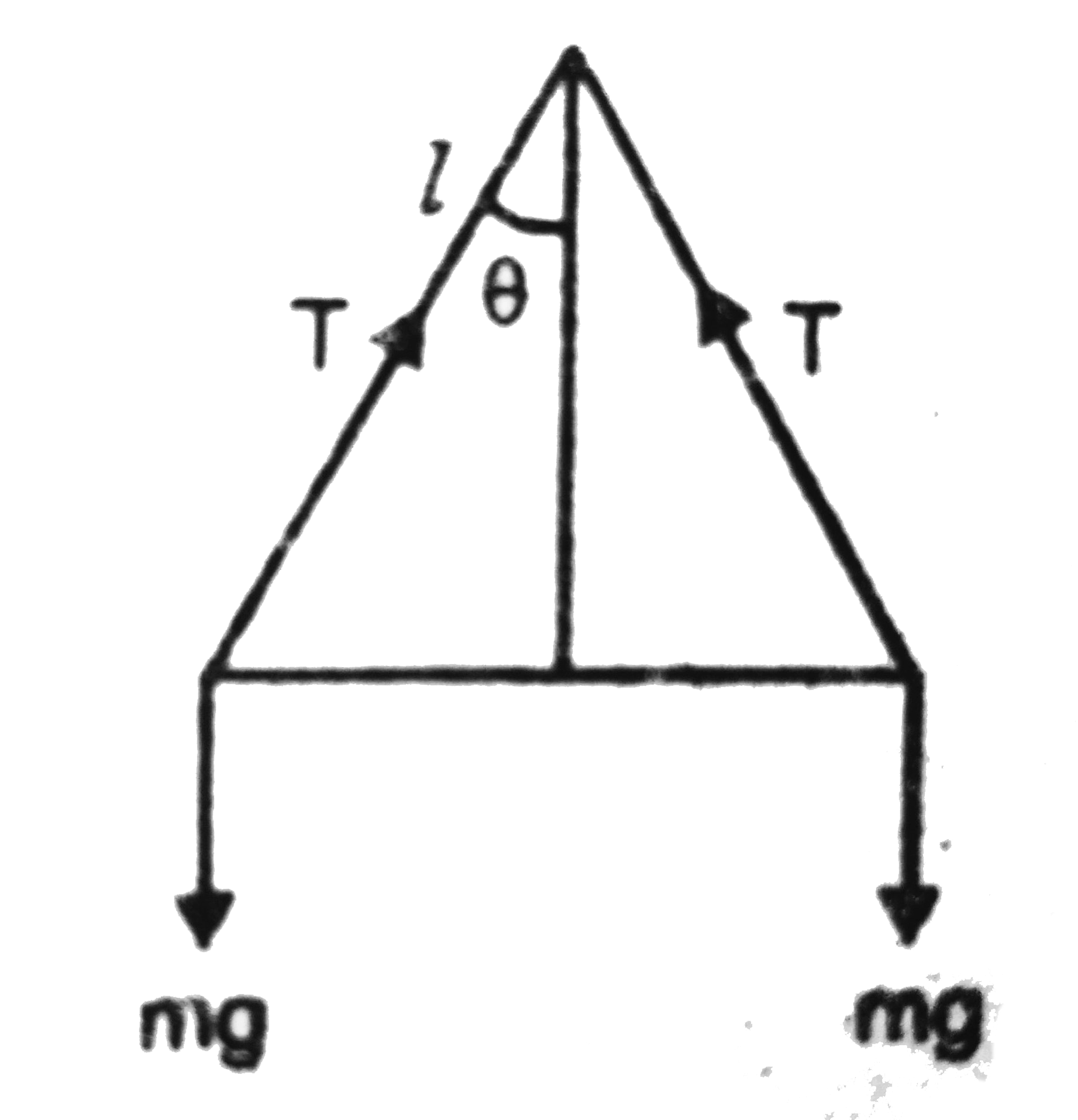
- Two identical pith balls are charged by rubbing against each other. T...
Text Solution
|
- Two small spheres, each having a mass of 20 g, are suspended form a co...
Text Solution
|
- Two indentical pith balls, each carrying charge q, are suspended from...
Text Solution
|
- A particle having a charge of 2.0xx10^(-4) C is placed directly below ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B having charges q and 2q respectively are placed ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identically charged particles are fastened to the two ends of a sp...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A having a charge of 2.0xx10 ^(-6) C is held fixed on a ho...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A having a charge of 2.0xx 10^(-6) C and a mass of 100 g i...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B having equal charges are placed at distance d ap...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B , ech carrying charge Q are held fixed with a se...
Text Solution
|
- Repeat the previous problem if the particle C s displaced through a di...
Text Solution
|
- The electric force experienced by a charge of 1.0xx10^(-6) C is 1.5 xx...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B having charges of +2.00 xx 10^(-6) C and of - 4....
Text Solution
|
- A Point charge produces an electric field in room ,What is its direct...
Text Solution
|
- A water particle of mass 10.0 mg and having a charge of 1.50 xx 10^(-6...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical charges, each having a value 1.0 xx10^(-8)C, are place...
Text Solution
|
- Positive charge Q is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of rad...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length L has a total charge Q distributed uniformly along its...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 cm long rod carries a charge of +150 muC distributed uniformly a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a uniformly charged ring of radius R. Find the pint on the ax...
Text Solution
|