Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ELECTRIC FIELD AND POTENTIAL-Exercises
- The bob of a simple pendulum has a mass of 40 g and a positive char...
Text Solution
|
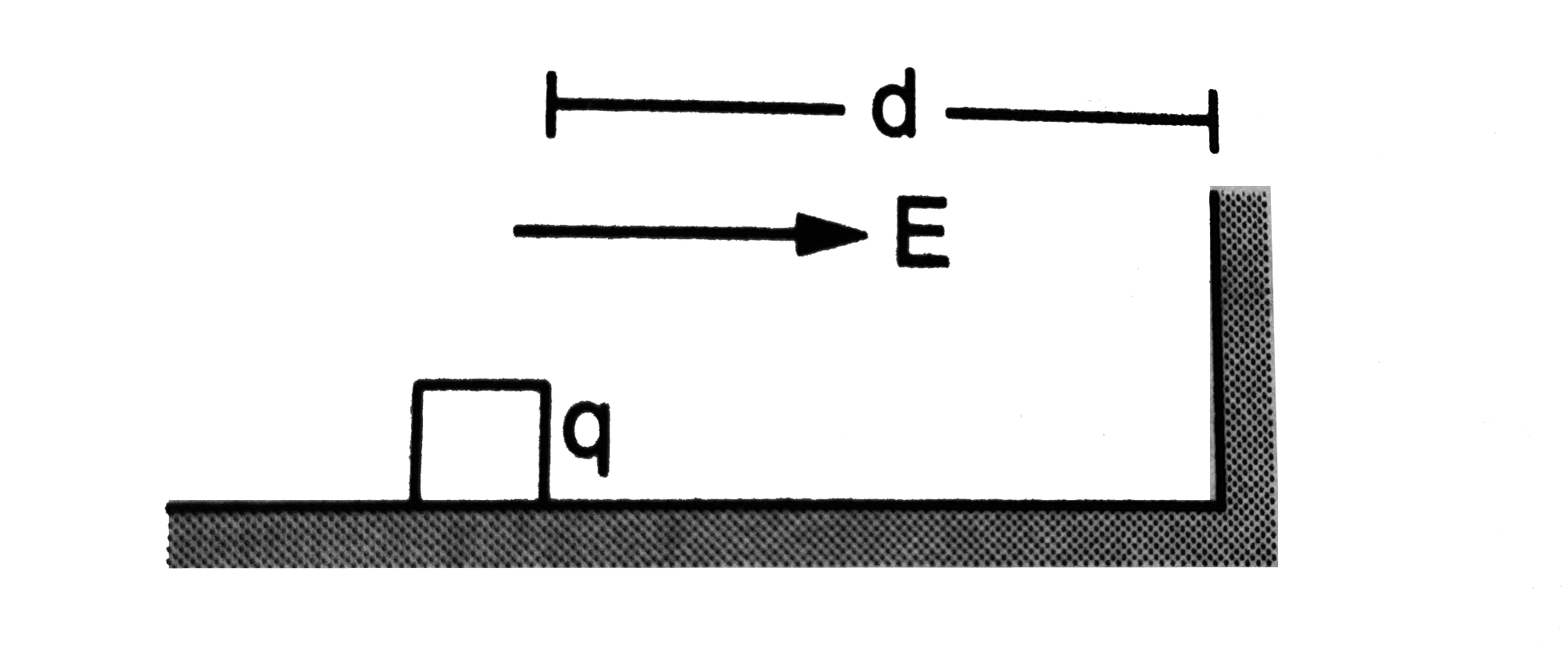
- A block of mass m having a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal t...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m containing a net positive charge q is placed on a sm...
Text Solution
|
- A Uniform electric field of 10NC ^(-1) exists in the vertically downwa...
Text Solution
|
- 12 j of work has to be done against an existion electric field to take...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal charges, 2.0xx10^(-7) C each, are held fixed at a separation...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field of 20 N//C exists along the x-axis in space. Calcula...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation of the previous problem. A charge of 2.0xx 10 ^...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field vecE = vec(i20 + vecj30 ) NC^(-1) exists in the spac...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field vecE = vec i Ax exists in the space, where A= 10 V ...
Text Solution
|
- The electric potential existing in space is V(x,y,z)= A (xy+ yz+zx).(a...
Text Solution
|
- Two charged particles, having equal charges of 2.0xx 10^(-5) C each, a...
Text Solution
|
- Some equipotential surfaces are shown in figure(29.E3) What can you sa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a circular ring of radius r, uniformly charged with linear ch...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field of magnitude 1000 NC ^(-1) is produced between two p...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform field of 2.0 NC^(-1) exists in space in x direction (a) Taki...
Text Solution
|
- How much work has to be done in assembling three charged particles at ...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetc energy of a chargd particle decreased by 10 J as it moves f...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical particles, each having a charge of 2.0xx10^(-4) C and ma...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles have equal masses of 5.0 g each and opposite charges of ...
Text Solution
|